Nonylphenol Polyethoxylates Enhance Adipose Deposition in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish
- PMID: 35202285
- PMCID: PMC8879477
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10020099
Nonylphenol Polyethoxylates Enhance Adipose Deposition in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish
Erratum in
-
Correction: Kassotis et al. Nonylphenol Polyethoxylates Enhance Adipose Deposition in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish. Toxics 2022, 10, 99.Toxics. 2022 Jun 22;10(7):345. doi: 10.3390/toxics10070345. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35878313 Free PMC article.
Abstract
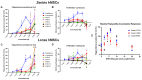
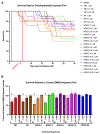
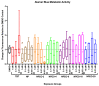
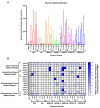
Alkylphenol polyethoxylates (APEOs), such as nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPEOs), are high-production-volume surfactants used in laundry detergents, hard-surface cleaners, pesticide formulations, textile production, oils, paints, and other products. NPEOs comprise -80% of the total production of APEOs and are widely reported across diverse environmental matrices. Despite a growing push for replacement products, APEOs continue to be released into the environment through wastewater at significant levels. Research into related nonionic surfactants from varying sources has reported metabolic health impacts, and we have previously demonstrated that diverse APEOs and alcohol polyethoxylates promote adipogenesis in the murine 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte model. These effects appeared to be independent of the base alkylphenol and related to the ethoxylate chain length, though limited research has evaluated NPEO exposures in animal models. The goals of this study were to assess the potential of NPEOs to promote adiposity (Nile red fluorescence quantification) and alter growth and/or development (toxicity, length, weight, and energy expenditure) of developmentally exposed zebrafish (Danio rerio). We also sought to expand our understanding of the ability to promote adiposity through evaluation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Herein, we demonstrated consistent adipogenic effects in two separate human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell models, and that nonylphenol and its ethoxylates promoted weight gain and increased adipose deposition in developmentally exposed zebrafish. Notably, across both cell and zebrafish models we report increasing adipogenic/obesogenic activity with increasing ethoxylate chain lengths up to maximums around NPEO-6 and then decreasing activity with the longest ethoxylate chain lengths. This research suggests metabolic health concerns for these common obesogens, suggesting further need to assess molecular mechanisms and better characterize environmental concentrations for human health risk assessments.
Keywords: adipogenesis; alkylphenol ethoxylates; endocrine disrupting chemicals; ethoxylated surfactants; mixtures; obesogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nonylphenol and Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Thyroid Hormone Receptor Signaling to Disrupt Metabolic Health.Endocrinology. 2024 Oct 30;165(12):bqae149. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae149. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39497475
-
Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Metabolic Health in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 28;13(3):359. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030359. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984799 Free PMC article.
-
Nonionic Ethoxylated Surfactants Induce Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2018 Mar 1;162(1):124-136. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx234. Toxicol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29106673 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactants in aquatic and terrestrial environment: occurrence, behavior, and treatment processes.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Feb;23(4):3195-216. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5803-x. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26590059 Review.
-
Obesity III: Obesogen assays: Limitations, strengths, and new directions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 May;199:115014. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115014. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35393121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Assessment of Proadipogenic Effects for Common-Use Contraceptives and Their Mixtures.Endocrinology. 2024 Apr 29;165(6):bqae050. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae050. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38648498 Free PMC article.
-
Nonylphenol and Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Thyroid Hormone Receptor Signaling to Disrupt Metabolic Health.Endocrinology. 2024 Oct 30;165(12):bqae149. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae149. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39497475
-
Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Metabolic Health in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 28;13(3):359. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030359. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984799 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity II: Establishing causal links between chemical exposures and obesity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 May;199:115015. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115015. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35395240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipogenic and endocrine disrupting mixture effects of organic and inorganic pollutant mixtures.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Jun 10;876:162587. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162587. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36871739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marcomini A., Filipuzzi F., Giger W. Aromatic surfactants in laundry detergents and hard-surface cleaners: Linear alkylbenzenesulphonates and alkylphenol polyethoxylates. Chemosphere. 1988;17:853–863. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(88)90058-6. - DOI
-
- Marcomini A., Stelluto S., Pavoni B. Determination of Linear Alkylbenzenesulphonates and Alkylphenol Polyethoxylates in Commercial Products and Marine Waters by Reversed- and Normal-Phase Hplc. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1989;35:207–218. doi: 10.1080/03067318908028395. - DOI
-
- Maguire R.J. Review of the Persistence of Nonylphenol and Nonylphenol Ethoxylates in Aquatic Environments. Water Qual. Res. J. 1999;34:37–78. doi: 10.2166/wqrj.1999.003. - DOI
-
- Loos R., Hanke G., Umlauf G., Eisenreich S.J. LC–MS–MS analysis and occurrence of octyl- and nonylphenol, their ethoxylates and their carboxylates in Belgian and Italian textile industry, waste water treatment plant effluents and surface waters. Chemosphere. 2007;66:690–699. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.060. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

