Detection of Anti- Neospora caninum Antibodies on Dairy Cattle Farms in Southern Italy
- PMID: 35202340
- PMCID: PMC8876793
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci9020087
Detection of Anti- Neospora caninum Antibodies on Dairy Cattle Farms in Southern Italy
Abstract
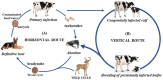
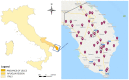
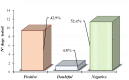
Neosporosis is recognized as one of the major causes of bovine abortion worldwide. Canids are the main definitive host for this parasite and the presence of dogs in the farm is an important factor for the Neospora caninum infection in bovines. Since, in the province of Lecce, located in the Apulia region of Southern Italy, there are no studies showing the presence of the infection in farm animals, the objective was to perform a serological evaluation for anti-N. caninum antibodiesin serum from 706 dairy cattle and 21 farm dogs located in 40 farms uniformlydistributed over the territory.The presence of N. caninum infection was confirmed in 90.0% (36/40) of the 40 farms examined. The results obtained on all serum samples by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ID Screen®Neospora caninum competition ELISA kit) for anti-N. caninum antibodies showed a seropositivity rate of 21.1% (149/706) among dairy cows, with a statistically significant higher percentage of positive subjects in the animals over two years old and a positivity rate of 42.9% (9/21) in tested dogs. The obtained data confirmed the presence of neosporosis even in the Lecce area, where it could therefore represent an important cause of abortion and economic losses.
Keywords: Italian cattle farms; Neospora caninum; serodiagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum in aborting dairy cattle in the Czech Republic.Vet Parasitol. 2003 Jul 29;115(3):239-45. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4017(03)00215-2. Vet Parasitol. 2003. PMID: 12935739
-
Seroprevalence and first multilocus microsatellite genotyping of Neospora caninum in dairy cattle in Henan, central China.Vet Parasitol. 2017 Sep 15;244:81-84. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.07.022. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Vet Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28917323
-
Risk factors for Neospora caninum infection in dairy cattle and their possible cause-effect relation for disease.Microb Pathog. 2017 Sep;110:202-207. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.06.042. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28666842
-
Immune response in bovine neosporosis: Protection or contribution to the pathogenesis of abortion.Microb Pathog. 2017 Aug;109:177-182. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.05.042. Epub 2017 May 31. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28578088 Review.
-
Neospora caninum in birds: A review.Parasitol Int. 2018 Aug;67(4):397-402. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Parasitol Int. 2018. PMID: 29614327 Review.
Cited by
-
An Antibody-Based Survey of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum Infection in Client-Owned Cats from Portugal.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 17;13(14):2327. doi: 10.3390/ani13142327. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508104 Free PMC article.
-
Serosurvey of selected reproductive pathogens in domestic ruminants from Upper Egypt.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Oct 23;10:1267640. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1267640. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37937151 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum in pet cats, dogs and rabbits from urban areas of Poland.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Jan 31;20(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03894-3. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38297328 Free PMC article.
-
Review of neosporosis: Disease insights and control approaches.Open Vet J. 2025 Mar;15(3):1078-1090. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i3.2. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Open Vet J. 2025. PMID: 40276172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Immunodiagnostic Performances of Neospora caninum Peroxiredoxin 2 (NcPrx2), Microneme 4 (NcMIC4), and Surface Antigen 1 (NcSAG1) Recombinant Proteins for Bovine Neosporosis.Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;14(4):531. doi: 10.3390/ani14040531. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396498 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

