Transmissible cancer influences immune gene expression in an endangered marsupial, the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii)
- PMID: 35202488
- PMCID: PMC9310804
- DOI: 10.1111/mec.16408
Transmissible cancer influences immune gene expression in an endangered marsupial, the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii)
Abstract
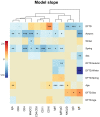
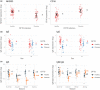
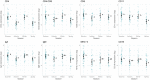
Understanding the effects of wildlife diseases on populations requires insight into local environmental conditions, host defence mechanisms, host life-history trade-offs, pathogen population dynamics, and their interactions. The survival of Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii) is challenged by a novel, fitness limiting pathogen, Tasmanian devil facial tumour disease (DFTD), a clonally transmissible, contagious cancer. In order to understand the devils' capacity to respond to DFTD, it is crucial to gain information on factors influencing the devils' immune system. By using RT-qPCR, we investigated how DFTD infection in association with intrinsic (sex and age) and environmental (season) factors influences the expression of 10 immune genes in Tasmanian devil blood. Our study showed that the expression of immune genes (both innate and adaptive) differed across seasons, a pattern that was altered when infected with DFTD. The expression of immunogbulins IgE and IgM:IgG showed downregulation in colder months in DFTD infected animals. We also observed strong positive association between the expression of an innate immune gene, CD16, and DFTD infection. Our results demonstrate that sampling across seasons, age groups and environmental conditions are beneficial when deciphering the complex ecoevolutionary interactions of not only conventional host-parasite systems, but also of host and diseases with high mortality rates, such as transmissible cancers.
Keywords: cancer; conservation physiology; host-parasite interactions; immune system; life history trade-off.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Ecology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Complex associations between cancer progression and immune gene expression reveals early influence of transmissible cancer on Tasmanian devils.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 7;15:1286352. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1286352. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38515744 Free PMC article.
-
Transmissible cancer and longitudinal telomere dynamics in Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii).Mol Ecol. 2022 Dec;31(24):6531-6540. doi: 10.1111/mec.16721. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Mol Ecol. 2022. PMID: 36205590 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglubolin dynamics and cancer prevalence in Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii).Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 29;6:25093. doi: 10.1038/srep25093. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27126067 Free PMC article.
-
Devil Facial Tumor Disease.Vet Pathol. 2016 Jul;53(4):726-36. doi: 10.1177/0300985815616444. Epub 2015 Dec 13. Vet Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26657222 Review.
-
Curse of the devil: molecular insights into the emergence of transmissible cancers in the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii).Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Jul;77(13):2507-2525. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03435-4. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31900624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
When Do Tumours Develop? Neoplastic Processes Across Different Timescales: Age, Season and Round the Circadian Clock.Evol Appl. 2024 Oct 22;17(10):e70024. doi: 10.1111/eva.70024. eCollection 2024 Oct. Evol Appl. 2024. PMID: 39444444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex associations between cancer progression and immune gene expression reveals early influence of transmissible cancer on Tasmanian devils.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 7;15:1286352. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1286352. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38515744 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the evolution of immune genes in jawed vertebrates.J Evol Biol. 2023 Jun;36(6):847-873. doi: 10.1111/jeb.14181. Epub 2023 May 31. J Evol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37255207 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aarøe, J. , Lindahl, T. , Dumeaux, V. , Sæbø, S. , Tobin, D. , Hagen, N. , Skaane, P. , Lönneborg, A. , Sharma, P. , & Børresen‐Dale, A.‐L. (2010). Gene expression profiling of peripheral blood cells for early detection of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research, 12(1), R7. 10.1186/bcr2472 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnould, L. , Gelly, M. , Penault‐Llorca, F. , Benoit, L. , Bonnetain, F. , Migeon, C. , Cabaret, V. , Fermeaux, V. , Bertheau, P. , Garnier, J. , Jeannin, J.‐F. , & Coudert, B. (2006). Trastuzumab‐based treatment of HER2‐positive breast cancer: An antibody‐dependent cellular cytotoxicity mechanism? British Journal of Cancer, 94(2), 259–267. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602930 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barton, K. (2020). MuMIn: Multi‐model inference. R package version 1.43.17. Retrieved from https://CRAN.R‐project.org/package=MuMIn
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

