Spike-timing-dependent plasticity rewards synchrony rather than causality
- PMID: 35203089
- PMCID: PMC9758582
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhac050
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity rewards synchrony rather than causality
Abstract
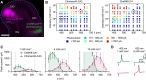
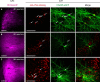
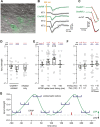
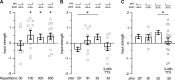
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is a candidate mechanism for information storage in the brain, but the whole-cell recordings required for the experimental induction of STDP are typically limited to 1 h. This mismatch of time scales is a long-standing weakness in synaptic theories of memory. Here we use spectrally separated optogenetic stimulation to fire precisely timed action potentials (spikes) in CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells. Twenty minutes after optogenetic induction of STDP (oSTDP), we observed timing-dependent depression (tLTD) and timing-dependent potentiation (tLTP), depending on the sequence of spiking. As oSTDP does not require electrodes, we could also assess the strength of these paired connections three days later. At this late time point, late tLTP was observed for both causal (CA3 before CA1) and anticausal (CA1 before CA3) timing, but not for asynchronous activity patterns (Δt = 50 ms). Blocking activity after induction of oSTDP prevented stable potentiation. Our results confirm that neurons wire together if they fire together, but suggest that synaptic depression after anticausal activation (tLTD) is a transient phenomenon.
Keywords: LTP; hippocampus; optogenetics; rat; synaptic plasticity.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Bing Z, Meschede C, Chen G, Knoll A, Huang K. Indirect and direct training of spiking neural networks for end-to-end control of a lane-keeping vehicle. Neural Netw. 2020:121:21–36. - PubMed
-
- Boyden ES, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat Neurosci. 2005:8:1263–1268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

