The Nephrotoxin Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induces Injury in Kidney Organoids Differentiated from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 35203286
- PMCID: PMC8870209
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11040635
The Nephrotoxin Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induces Injury in Kidney Organoids Differentiated from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: Nguyen et al. The Nephrotoxin Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induces Injury in Kidney Organoids Differentiated from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 635.Cells. 2022 Jun 21;11(13):1980. doi: 10.3390/cells11131980. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805209 Free PMC article.
Abstract
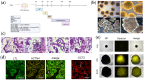
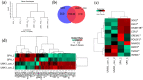
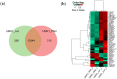
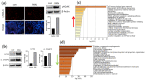
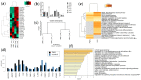
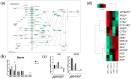
Kidney diseases, including acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), which can progress to end stage renal disease (ESRD), are a worldwide health burden. Organ transplantation or kidney dialysis are the only effective available therapeutic tools. Therefore, in vitro models of kidney diseases and the development of prospective therapeutic options are urgently needed. Within the kidney, the glomeruli are involved in blood filtration and waste excretion and are easily affected by changing cellular conditions. Puromycin aminonucleoside (PAN) is a nephrotoxin, which can be employed to induce acute glomerular damage and to model glomerular disease. For this reason, we generated kidney organoids from three iPSC lines and treated these with PAN in order to induce kidney injury. Morphological observations revealed the disruption of glomerular and tubular structures within the kidney organoids upon PAN treatment, which were confirmed by transcriptome analyses. Subsequent analyses revealed an upregulation of immune response as well as inflammatory and cell-death-related processes. We conclude that the treatment of iPSC-derived kidney organoids with PAN induces kidney injury mediated by an intertwined network of inflammation, cytoskeletal re-arrangement, DNA damage, apoptosis and cell death. Furthermore, urine-stem-cell-derived kidney organoids can be used to model kidney-associated diseases and drug discovery.
Keywords: AKI; DNA damage; RAAS; apoptosis; iPSCs; inflammation; organoids; puromycin aminonucleoside; urine cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou Y., Kim C., Lorenzo J., Pablo B., Zhang F., Jung J.Y., Xiao L., Bazua S., Emani M., Hopkins C., et al. Blocking the Rac1-TRPC5 Pathway Protects Human Podocytes. bioRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2020.08.28.272344. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

