Role of Dietary Supplements and Probiotics in Modulating Microbiota and Bone Health: The Gut-Bone Axis
- PMID: 35203401
- PMCID: PMC8870226
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11040743
Role of Dietary Supplements and Probiotics in Modulating Microbiota and Bone Health: The Gut-Bone Axis
Abstract
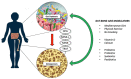
Osteoporosis is characterized by an alteration of bone microstructure with a decreased bone mineral density, leading to the incidence of fragility fractures. Around 200 million people are affected by osteoporosis, representing a major health burden worldwide. Several factors are involved in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Today, altered intestinal homeostasis is being investigated as a potential additional risk factor for reduced bone health and, therefore, as a novel potential therapeutic target. The intestinal microflora influences osteoclasts' activity by regulating the serum levels of IGF-1, while also acting on the intestinal absorption of calcium. It is therefore not surprising that gut dysbiosis impacts bone health. Microbiota alterations affect the OPG/RANKL pathway in osteoclasts, and are correlated with reduced bone strength and quality. In this context, it has been hypothesized that dietary supplements, prebiotics, and probiotics contribute to the intestinal microecological balance that is important for bone health. The aim of the present comprehensive review is to describe the state of the art on the role of dietary supplements and probiotics as therapeutic agents for bone health regulation and osteoporosis, through gut microbiota modulation.
Keywords: bone health; dietary supplements; gut microbiota; microbiota; osteoporosis; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The potential mechanism of the microbiota-gut-bone axis in osteoporosis: a review.Osteoporos Int. 2022 Dec;33(12):2495-2506. doi: 10.1007/s00198-022-06557-x. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Osteoporos Int. 2022. PMID: 36169678 Review.
-
The Human Gut Microbiota: A Key Mediator of Osteoporosis and Osteogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 31;22(17):9452. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179452. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are Probiotics the New Calcium and Vitamin D for Bone Health?Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020 Jun;18(3):273-284. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00591-6. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020. PMID: 32285249 Review.
-
Crosstalk between the gut microbiota and postmenopausal osteoporosis: Mechanisms and applications.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Sep;110:108998. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108998. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35785728 Review.
-
The regulative effect and repercussion of probiotics and prebiotics on osteoporosis: involvement of brain-gut-bone axis.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(25):7510-7528. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2047005. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35234534 Review.
Cited by
-
The Prevalence of Dietary Supplements That Claim Estrogen-like Effects in Japanese Women.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 26;14(21):4509. doi: 10.3390/nu14214509. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364772 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the Probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis HN019 in Oral Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 19;23(16):9334. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169334. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbiome's role in musculoskeletal health through the gut-bone axis insights.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2410478. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2410478. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39387683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Probiotics and Gut Microbiota on Bone Metabolism in Chickens: A Review.Metabolites. 2022 Oct 20;12(10):1000. doi: 10.3390/metabo12101000. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36295902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Triangular Relationship among Diet-Gut Microbiota-Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9366. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179366. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

