Comparison of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy with Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection for Early Osteoarthritis of the Knees
- PMID: 35203417
- PMCID: PMC8869751
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020202
Comparison of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy with Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection for Early Osteoarthritis of the Knees
Abstract
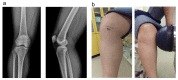
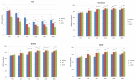
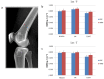
Conservative treatments for early osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee included the use of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and intra-articular hyaluronic acid (HA) injection. Recently, several animal studies reported that extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) demonstrated chondroprotective effects on knee OA. The present study compared the efficacy of oral NSAIDs, HA injection, and noninvasive ESWT for early OA of the knee. Forty-five patients with early knee OA were randomized into three groups. NSAIDs group received celecoxib 200 mg daily for 3 weeks. HA group received intra-articular injection of HA once a week for 3 weeks. ESWT group received ESWT for 3 sessions at bi-weekly interval. All patients were followed up for one year. Evaluations included the visual analogue scale (VAS) score, serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), plain radiography, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In addition, the functional scores were performed including, WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index) score, KOOS (knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome) score, and IKDC (International Knee Documentation Committee) score. All three groups showed significant improvement in VAS and functional scores as well as in the collected one-year follow-up data after treatments. ESWT group had better pain relief than NSAIDs and HA groups. ESWT group had better therapeutic effects in the functional scores than NSAIDs and HA groups. The bone mineral density (BMD) of proximal tibia is significantly increased after ESWT than others. In the serum ELISA, ESWT inhibited the expression of COMP in knee OA patients as compared with NSAIDs and HA groups. The parameters of MRI showed no significant differences between three groups after treatments. ESWT and intra-articular HA injection showed comparable results than NSAIDs. ESWT was superior in pain relief than HA and NSAIDs. The results demonstrated that ESWT was an effective and alternative therapy than HA and NSAIDs for early osteoarthritis of the knees.
Keywords: extracorporeal shockwave therapy; hyaluronic acid; knee; non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of a Single Intra-articular Injection of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid Versus NSAIDs on the Visual Analog Pain Scale and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index Scores in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis.Cureus. 2024 Sep 13;16(9):e69313. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69313. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39398745 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular viscosupplementation with hylan g-f 20 to treat osteoarthritis of the knee: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(10):1-66. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074461 Free PMC article.
-
An Open-Labeled Randomized Prospective Multi-center Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Intra-articular Injection of OSSINEXT™, an Autologous Growth Factor Concentrate (AGFC) Compared to Hyaluronic Acid (HA) in Knee Osteoarthritis.Cureus. 2022 Nov 3;14(11):e31058. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31058. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36475131 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Sep 11;15(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01919-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32912243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Jan;49(1):249-260. doi: 10.1177/0363546520909397. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 32302218
Cited by
-
Comparative Efficacy of Intra-Articular Injection, Physical Therapy, and Combined Treatments on Pain, Function, and Sarcopenia Indices in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 23;24(7):6078. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076078. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047058 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative analysis of platelet-rich plasma alone versus combined with extracorporeal shockwave therapy in athletes with patellar tendinopathy and knee pain: a randomized controlled trial.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024 Dec 17;36(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s43019-024-00252-3. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39690426 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for knee osteoarthritis : an umbrella review.Int J Surg. 2024 Apr 1;110(4):2389-2395. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001116. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38668665 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Non-Operative Interventions for Anterior Knee Pain.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2024 Dec;17(12):589-615. doi: 10.1007/s12178-024-09930-x. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2024. PMID: 39527393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of the use of shockwave therapy for knee osteoarthritis.J Orthop. 2024 May 1;56:18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2024.04.020. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38765896 Review.
References
-
- Cheng J.-H., Hsu C.-C., Hsu S.-L., Chou W.-Y., Wu Y.-N., Kuo C.-E.A., Hsu T.-C., Shiu L.-Y., Jhan S.-W. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Conditioned Medium Modulates the Expression of Inflammation Induced Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2, -5 and -6 as Well as Compared with Shockwave Therapy on Rat Knee Osteoarthritis. Biomedicines. 2021;9:1399. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101399. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

