Targeting NF-κB Signaling in Cancer Stem Cells: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35203471
- PMCID: PMC8869483
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020261
Targeting NF-κB Signaling in Cancer Stem Cells: A Narrative Review
Abstract
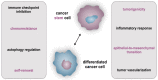
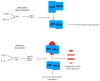
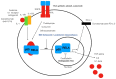
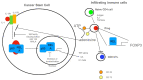
Among the cell populations existing within a tumor, cancer stem cells are responsible for metastasis formation and chemotherapeutic resistance. In the present review, we focus on the transcription factor NF-κB, which is present in every cell type including cancer stem cells. NF-κB is involved in pro-tumor inflammation by its target gene interleukin 1 (IL1) and can be activated by a feed-forward loop in an IL1-dependent manner. Here, we summarize current strategies targeting NF-κB by chemicals and biologicals within an integrated cancer therapy. Specifically, we start with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting epidermal growth factor (EGF)-receptor-mediated phosphorylation. Furthermore, we summarize current strategies of multiple myeloma treatment involving lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone as potential NF-κB inhibitors. Finally, we discuss programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) as an NF-κB target gene and its role in checkpoint therapy. We conclude, that NF-κB inhibition by specific inhibitors of IκB kinase was of no clinical use but inhibition of upstream and downstream targets with drugs or biologicals might be a fruitful way to treat cancer stem cells.
Keywords: EGF; NF-κB; PD-L1; bortezomib; cancer stem cells; dexamethasone; lenalidomide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wyckoff J., Wang W., Lin E.Y., Wang Y., Pixley F., Stanley E.R., Graf T., Pollard J.W., Segall J., Condeelis J. A Paracrine Loop between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Is Required for Tumor Cell Migration in Mammary Tumors. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7022–7029. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1449. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

