Vitisin A, a Resveratrol Tetramer, Improves Scopolamine-Induced Impaired Learning and Memory Functions in Amnesiac ICR Mice
- PMID: 35203483
- PMCID: PMC8869728
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020273
Vitisin A, a Resveratrol Tetramer, Improves Scopolamine-Induced Impaired Learning and Memory Functions in Amnesiac ICR Mice
Abstract
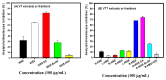
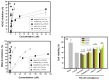
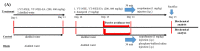
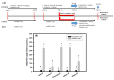
Resveratrol has been reported to exhibit neuroprotective activities in vitro and in vivo. However, little is known about resveratrol tetramers of hopeaphenol, vitisin A, and vitisin B with the same molecular mass in the improvement of degenerative disorders. In this study, two 95% ethanol extracts (95EE) from stem parts of Vitis thunbergii Sieb. & Zucc. (VT-95EE) and from the root (R) parts of Vitis thunbergii var. taiwaniana (VTT-R-95EE) showed comparable acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory activities. It was found that VT-95EE and VTT-R-95EE showed different distribution patterns of identified resveratrol and resveratrol tetramers of hopeaphenol, vitisin A, and vitisin B based on the analyses of HPLC chromatographic profiles. The hopeaphenol, vitisin A, and vitisin B, showed AChE and monoamine oxidase-B inhibitions in a dose-dependent manner, among which vitisin B and vitisin A exhibited much better activities than those of resveratrol, and had neuroprotective activities against methylglyoxal-induced SH-SY5Y cell deaths. The scopolamine-induced amnesiac ICR mice treated with VT-95EE and its ethyl acetate-partitioned fraction (VT-95EE-EA) at doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg, or vitisin A at a dose of 40 mg/kg, but not vitisin B (40 mg/kg), were shown significantly to improve the impaired learning behaviors by passive avoidance tests compared to those in the control without drug treatments (p < 0.05). Compared to mice in the control group, the brain extracts in the vitisin A-treated mice or donepezil-treated mice showed significant reductions in AChE activities and malondialdehyde levels (p < 0.05), and elevated the reduced protein expressions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and BDNF receptor, tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB). These results revealed that vitisin A was the active constituent in the VT-95EE and VTT-95EE, and the VT medicinal plant and that the endemic variety of VTT has potential in developing functional foods for an unmet medical need for neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: acetylcholinesterase; brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); scopolamine; vitisin A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vitisin B, a resveratrol tetramer from Vitis thunbergii var. taiwaniana, ameliorates impaired glucose regulations in nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice.J Tradit Complement Med. 2023 May 30;13(5):479-488. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.05.003. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Tradit Complement Med. 2023. PMID: 37693102 Free PMC article.
-
Vitis thunbergii var. taiwaniana Extracts and Purified Compounds Ameliorate Obesity in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Oct 28;63(42):9286-94. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04269. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26448517
-
Anti-α-glucosidase and Anti-dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Activities of Extracts and Purified Compounds from Vitis thunbergii var. taiwaniana.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Jul 22;63(28):6393-401. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02069. Epub 2015 Jul 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26138774
-
Cytotoxicity of (-)-vitisin B in human leukemia cells.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2013 Jul;36(3):313-9. doi: 10.3109/01480545.2012.720990. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23030068
-
The central administration of vitisin a, extracted from Vitis vinifera, improves cognitive function and related signaling pathways in a scopolamine-induced dementia model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114812. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114812. Epub 2023 May 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37148861
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase and Amyloid-β Aggregation by Piceatannol and Analogs: Assessing In Vitro and In Vivo Impact on a Murine Model of Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 29;12(7):1362. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071362. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507902 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Activity of Oligomeric Stilbenes from Alpha Grape Stems in In Vitro Models of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 7;26(6):2411. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062411. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141054 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Neurological Disorders with Stilbenes: Bridging the Preclinical-Clinical Gap.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Oct 7;20(14):5474-5494. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.102032. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39494329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracts and Scirpusin B from Recycled Seeds and Rinds of Passion Fruits (Passiflora edulis var. Tainung No. 1) Exhibit Improved Functions in Scopolamine-Induced Impaired-Memory ICR Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;12(12):2058. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122058. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136179 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant, anti-acetylcholinesterase, and anti-amyloid-β peptide aggregations of hispolon and its analogs in vitro and improved learning and memory functions in scopolamine-induced ICR mice.Bot Stud. 2024 Dec 18;65(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40529-024-00443-x. Bot Stud. 2024. PMID: 39692936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Dementia. 2019. [(accessed on 26 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia.
-
- Plassman B.L., Lang K.M., Fisher G.G., Heeringa S.G., Weir D.R., Ofstedal M.B., Burke J.R., Hurd M.D., Potter G.G., Rodgers W.L., et al. Prevalence of dementia in the United States: The aging, demographics, and memory study. Neuroepidemiology. 2007;29:125–132. doi: 10.1159/000109998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

