Genetic Complementation of ATP Synthase Deficiency Due to Dysfunction of TMEM70 Assembly Factor in Rat
- PMID: 35203486
- PMCID: PMC8869460
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020276
Genetic Complementation of ATP Synthase Deficiency Due to Dysfunction of TMEM70 Assembly Factor in Rat
Abstract
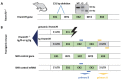
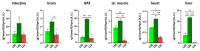
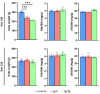
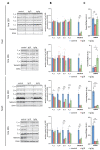
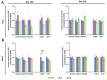
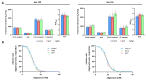
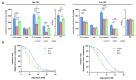
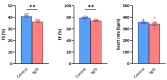
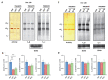
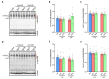
Mutations of the TMEM70 gene disrupt the biogenesis of the ATP synthase and represent the most frequent cause of autosomal recessive encephalo-cardio-myopathy with neonatal onset. Patient tissues show isolated defects in the ATP synthase, leading to the impaired mitochondrial synthesis of ATP and insufficient energy provision. In the current study, we tested the efficiency of gene complementation by using a transgenic rescue approach in spontaneously hypertensive rats with the targeted Tmem70 gene (SHR-Tmem70ko/ko), which leads to embryonic lethality. We generated SHR-Tmem70ko/ko knockout rats expressing the Tmem70 wild-type transgene (SHR-Tmem70ko/ko,tg/tg) under the control of the EF-1α universal promoter. Transgenic rescue resulted in viable animals that showed the variable expression of the Tmem70 transgene across the range of tissues and only minor differences in terms of the growth parameters. The TMEM70 protein was restored to 16-49% of the controls in the liver and heart, which was sufficient for the full biochemical complementation of ATP synthase biogenesis as well as for mitochondrial energetic function in the liver. In the heart, we observed partial biochemical complementation, especially in SHR-Tmem70ko/ko,tg/0 hemizygotes. As a result, this led to a minor impairment in left ventricle function. Overall, the transgenic rescue of Tmem70 in SHR-Tmem70ko/ko knockout rats resulted in the efficient complementation of ATP synthase deficiency and thus in the successful genetic treatment of an otherwise fatal mitochondrial disorder.
Keywords: ATP synthase deficiency; TMEM70 factor; gene therapy; mitochondria disease; transgenic rescue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

