Identification and Characterization of Besifovir-Resistant Hepatitis B Virus Isolated from a Chronic Hepatitis B Patient
- PMID: 35203489
- PMCID: PMC8868672
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020282
Identification and Characterization of Besifovir-Resistant Hepatitis B Virus Isolated from a Chronic Hepatitis B Patient
Abstract
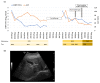
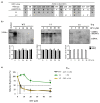
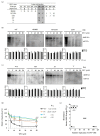
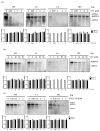
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is known to cause severe liver diseases such as acute or chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection is a major health problem with nearly 300 million individuals infected worldwide. Currently, nucleos(t)ide analogs (NAs) and interferon alpha are clinically approved treatments for HBV infection. NAs are potent antiviral agents that bind to HBV polymerase and block viral reverse transcription and replication. Besifovir dipivoxil maleate (BSV) is a newly developed NA against HBV in the form of acyclic nucleotide phosphonate that is available for oral administration similar to adefovir and tenofovir. Until now, resistance to BSV treatment has not been reported. In this study, we found a CHB patient who showed viral breakthrough after long-term treatment with BSV. The isolated HBV DNA from patient's serum were cloned into the replication-competent HBV 1.2 mer and the sequence of reverse transcriptase (RT) domain of HBV polymerase were analyzed. We also examined the drug susceptibility of generated clones in vitro. Several mutations were identified in HBV RT domain. A particular mutant harboring ten RT mutations showed resistance to BSV treatment in vitro. The ten mutations include rtV23I (I), rtH55R (R), rtY124H (H), rtD134E (E), rtN139K (K), rtL180M (M), rtM204V (V), rtQ267L (L), rtL269I (I) and rtL336M (M). To further identify the responsible mutations for BSV resistance, we performed in vitro drug susceptibility assay on several artificial clones. As a result, our study revealed that rtL180M (M) and rtM204V (V) mutations, already known as lamivudine-resistant mutations, confer resistance to BSV in the CHB patient.
Keywords: besifovir dipivoxil maleate (BSV); drug resistance; hepatitis B virus; nucleos(t)ide analog; reverse transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest relevant to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Sun Y., Wang S., Yi Y., Zhang J., Duan Z., Yuan K., Liu W., Li J., Zhu Y. The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Binding Protein: An Immunoglobulin G Constant Region-Like Protein That Interacts With HBV Envelop Proteins and Mediates HBV Entry. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018;8:338. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00338. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tu T., Budzinska M.A., Vondran F.W.R., Shackel N.A., Urban S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration Occurs Early in the Viral Life Cycle in an In Vitro Infection Model via Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide-Dependent Uptake of Enveloped Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2018;92:e02007-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02007-17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ko C., Chakraborty A., Chou W.M., Hasreiter J., Wettengel J.M., Stadler D., Bester R., Asen T., Zhang K., Wisskirchen K., et al. Hepatitis B virus genome recycling and de novo secondary infection events maintain stable cccDNA levels. J. Hepatol. 2018;69:1231–1241. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

