Bacterial-Specific Induction of Inflammatory Cytokines Significantly Decreases upon Dual Species Infections of Implant Materials with Periodontal Pathogens in a Mouse Model
- PMID: 35203495
- PMCID: PMC8869624
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020286
Bacterial-Specific Induction of Inflammatory Cytokines Significantly Decreases upon Dual Species Infections of Implant Materials with Periodontal Pathogens in a Mouse Model
Abstract
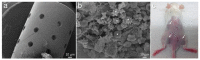
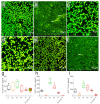
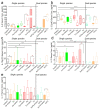
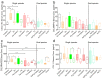
Cytokine profiles are often perturbed after infections of medical implants. With a non-invasive in vivo imaging system, we report in a mouse model that interferon expression after infection of subcutaneous implants with Streptococcus oralis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Treponema denticola (alone or as a combination) was species-specific, persisted longer in the presence of implants, and notably decreased upon dual species infections. This type I interferon expression disappeared within two weeks; however, histology of implant-tissue interface indicated high recruitment of immune cells even after three weeks. This was suggestive that biomaterial-associated infections could have prolonged effects, including the systemic stimulation of inflammatory cytokines. The present study investigated the systemic impact of this chronic peri-implant inflammation on the systemic expression of inflammatory cytokines (23) using a multiplex assay. Initially, the cytokine measurement in murine fibroblasts exposed to periodontal pathogens remained limited to the expression of five cytokines, namely, IL-6, G-CSF, CXCL-1/KC, MCP-1 (MCAF), and IL-12 (p40). The systemic determination of cytokines in mice increased to 19 cytokines (IL-1α, IL-2, IL-3, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-12 (p40), IL-12 (p70), IL-13, IL-17A, CCL-11/Eotaxin, G-CSF, IFN-γ, CXCL1/KC, MCP-1 (MCAF), MIP-1α/CCL3, MIP-1β/CCL4, CCL5/RANTES, and TNF-α). Systemic induction of cytokines was species-specific in the mouse model. The cytokine induction from infected implants differed significantly from sole tissue infections and sterile implants. Notably, systemic cytokine induction decreased after infections with dual species compared to single species infections. These findings describe the systemic effect of chronic peri-implant inflammation on the systemic induction of inflammatory cytokines, and this effect was strongly correlated to the type and composition of initial infection. Systemic modulations in cytokine expression upon dual species infections exhibit an exciting pattern that might explain the complications associated with biomaterial-related infection in patients. Moreover, these findings validate the requirement of multispecies infections for pre-clinical studies involving animal models.
Keywords: biomaterial-associated infections; cytokine; fibroblasts; mouse model; periodontal pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest (such as a financial relationship with one or more companies whose products are featured in the manuscript).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiplex determination of murine seminal fluid cytokine profiles.Reproduction. 2006 Mar;131(3):613-21. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00959. Reproduction. 2006. PMID: 16514204
-
Non-Invasive Luciferase Imaging of Type I Interferon Induction in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Biomaterial Associated Bacterial Infections: Microbial Specificity and Inter-Bacterial Species Interactions.Microorganisms. 2020 Oct 21;8(10):1624. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8101624. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33096869 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of titanium implants along with silver ions and tetracycline on type I interferon-beta expression during implant-related infections in co-culture and mouse model.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 19;11:1227148. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1227148. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37929187 Free PMC article.
-
Uterine and serum cytokine arrays in the mouse during estrus.Anim Reprod Sci. 2007 Aug;100(3-4):301-10. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2006.08.016. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Anim Reprod Sci. 2007. PMID: 16963201
-
Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002;8:6-48. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12690937 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial of Special Issue "Pharmacomicrobiomics in Non-Communicable Disease".Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 6;10(7):1605. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071605. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884910 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Inflammatory Factors and Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Analysis in Patients with Kawasaki Disease.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2025 Mar 12;21:99-108. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S509753. eCollection 2025. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2025. PMID: 40092571 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulation in Non-traditional Therapies for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Management.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Sep 6;81(10):346. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03875-7. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39240286 Review.
-
Sonopermeation combined with stroma normalization enables complete cure using nano-immunotherapy in murine breast tumors.J Control Release. 2025 Jun 10;382:113722. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113722. Epub 2025 Apr 14. J Control Release. 2025. PMID: 40233830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghensi P., Manghi P., Zolfo M., Armanini F., Pasolli E., Bolzan M., Bertelle A., Dell’Acqua F., Dellasega E., Waldner R., et al. Strong oral plaque microbiome signatures for dental implant diseases identified by strain-resolution metagenomics. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes. 2020;6:47. doi: 10.1038/s41522-020-00155-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kabir L., Stiesch M., Grischke J. The effect of keratinized mucosa on the severity of peri-implant mucositis differs between periodontally healthy subjects and the general population: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021;25:1183–1193. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03422-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bremer F., Grade S., Kohorst P., Stiesch M. In vivo biofilm formation on different dental ceramics. Quintessence Int. 2011;42:565–574. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

