Impact of Adalimumab Treatment on Interleukin-17 and Interleukin-17 Receptor Expression in Skin and Synovium of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients with Mild Psoriasis
- PMID: 35203534
- PMCID: PMC8869729
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020324
Impact of Adalimumab Treatment on Interleukin-17 and Interleukin-17 Receptor Expression in Skin and Synovium of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients with Mild Psoriasis
Abstract
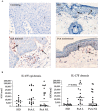
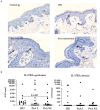
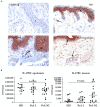
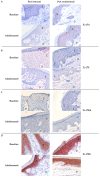
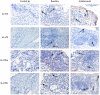
Interleukin (IL)-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF)-α are key players in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) pathogenesis. While both cytokines can be therapeutically targeted with beneficial clinical outcome, it is unclear whether inhibiting one cytokine will affect the other at sites of inflammation. If both act independently, this might provide a rationale for dual or combined inhibition of both cytokines. Here, we evaluated the effect of TNF blockade in PsA patients on IL-17 levels in both skin and synovial tissue biopsies. PsA patients with mild psoriatic skin lesions were randomized to receive either adalimumab or placebo for four weeks. Synovial and skin biopsies were obtained at weeks zero and four. Skin from healthy donors (HDs) was used for comparison. Expression of IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-17RA and IL-17RC was assessed by immunohistochemistry and analyzed with digital image analysis. We found relatively low levels of IL-17 and its receptors in the skin of PsA patients compared to HD, and only IL-17F in the dermis of lesional psoriatic skin was significantly higher compared to HD skin (p = 0.0002). Histologically IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-17RA and IL-17RC in skin and synovial tissue were not downregulated by adalimumab treatment. Thus, in this cohort of PsA patients with mild psoriasis, TNF blockade did not affect the protein levels of IL-17 cytokines and its receptors in skin and synovium, despite reduced cellular inflammation and improved clinical outcome for joint involvement.
Keywords: adalimumab; immunohistochemistry; immunopathogenesis; interleukin-17; psoriatic arthritis; skin; synovium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no competing interests. DMG is currently working at UCBpharma and PPT is currently working at Candel Therapeutics, both companies had no role in this project.
Figures

References
-
- Xu X., Davelaar N., Mus A., Asmawidjaja P.S., Hazes J.M.W., Baeten D.L.P., Vis M., Bisoendial R.J., Prens E.P., Lubberts E. Interleukin-17A Is Produced by CD4+ but Not CD8+ T Cells in Synovial Fluid Following T Cell Receptor Activation and Regulates Different Inflammatory Mediators Compared to Tumor Necrosis Factor in a Model of Psoriatic Arthritis Synovitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72:1303–1313. doi: 10.1002/art.41271. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

