Dysregulation of β-Cell Proliferation in Diabetes: Possibilities of Combination Therapy in the Development of a Comprehensive Treatment
- PMID: 35203680
- PMCID: PMC8962301
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10020472
Dysregulation of β-Cell Proliferation in Diabetes: Possibilities of Combination Therapy in the Development of a Comprehensive Treatment
Abstract
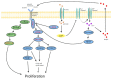
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia as a result of insufficient insulin levels and/or impaired function as a result of autoimmune destruction or insulin resistance. While Type 1 DM (T1DM) and Type 2 DM (T2DM) occur through different pathological processes, both result in β-cell destruction and/or dysfunction, which ultimately lead to insufficient β-cell mass to maintain normoglycemia. Therefore, therapeutic agents capable of inducing β-cell proliferation is crucial in treating and reversing diabetes; unfortunately, adult human β-cell proliferation has been shown to be very limited (~0.2% of β-cells/24 h) and poorly responsive to many mitogens. Furthermore, diabetogenic insults result in damage to β cells, making it ever more difficult to induce proliferation. In this review, we discuss β-cell mass/proliferation pathways dysregulated in diabetes and current therapeutic agents studied to induce β-cell proliferation. Furthermore, we discuss possible combination therapies of proliferation agents with immunosuppressants and antioxidative therapy to improve overall long-term outcomes of diabetes.
Keywords: antioxidative therapy; diabetes; immunosuppression; pancreatic β-cells; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Disease, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney. National Institute of Health; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2020.
-
- Utzschneider K.M., Younes N., Rasouli N., Barzilay J.I., Banerji M.A., Cohen R.M., Gonzalez E.V., Ismail-Beigi F., Mather K.J., Raskin P., et al. Shape of the Ogtt Glucose Response Curve: Relationship with Beta-Cell Function and Differences by Sex, Race, and Bmi in Adults with Early Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Metformin. BMJ Open Diabet. Res. Care. 2021;9:e002264. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

