Strategies to Limit Cognitive Impairments under Sleep Restriction: Relationship to Stress Biomarkers
- PMID: 35203992
- PMCID: PMC8869873
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12020229
Strategies to Limit Cognitive Impairments under Sleep Restriction: Relationship to Stress Biomarkers
Abstract
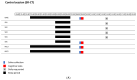
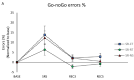
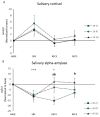
Adding relaxation techniques during nap or auditory stimulation of EEG slow oscillation (SO) during nighttime sleep may limit cognitive impairments in sleep-deprived subjects, potentially through alleviating stress-releasing effects. We compared daytime sleepiness, cognitive performances, and salivary stress biomarker responses in 11 volunteers (aged 18-36) who underwent 5 days of sleep restriction (SR, 3 h per night, with 30 min of daily nap) under three successive conditions: control (SR-CT), relaxation techniques added to daily nap (SR-RT), and auditory stimulation of sleep slow oscillations (SO) during nighttime sleep (SR-NS). Test evaluation was performed at baseline (BASE), the fifth day of chronic SR (SR5), and the third and fifth days after sleep recovery (REC3, REC5, respectively). At SR5, less degradation was observed for percentage of commission errors in the executive Go-noGo inhibition task in SR-RT condition compared to SR-CT, and for sleepiness score in SR-NS condition compared both to SR-CT and SR-RT. Beneficial effects of SR-RT and SR-NS were additionally observed on these two parameters and on salivary α-amylase (sAA) at REC3 and REC5. Adding relaxation techniques to naps may help performance in inhibition response, and adding nocturnal auditory stimulation of SO sleep may benefit daytime sleepiness during sleep restriction with persistent effects during recovery. The two strategies activated the autonomic nervous system, as shown by the sAA response.
Keywords: auditory EEG slow oscillation; cognition; recovery; relaxation technique; sleep-deprived; stress biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Rabat A., Gomez-Merino D., Roca-Paixao L., Bougard C., Van Beers P., Dispersyn G., Guillard M., Bourrilhon C., Drogou C., Arnal P.J., et al. Differential Kinetics in Alteration and Recovery of Cognitive Processes from a Chronic Sleep Restriction in Young Healthy Men. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016;10:95. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

