Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB)-Forming Phytoplankton and Their Potential Impact on Surrounding Living Organisms
- PMID: 35204089
- PMCID: PMC8868398
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11020206
Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB)-Forming Phytoplankton and Their Potential Impact on Surrounding Living Organisms
Abstract
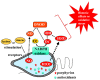
Most marine phytoplankton with relatively high ROS generation rates are categorized as harmful algal bloom (HAB)-forming species, among which Chattonella genera is the highest ROS-producing phytoplankton. In this review, we examined marine microalgae with ROS-producing activities, with focus on Chattonella genera. Several studies suggest that Chattonella produces superoxide via the activities of an enzyme similar to NADPH oxidase located on glycocalyx, a cell surface structure, while hydrogen peroxide is generated inside the cell by different pathways. Additionally, hydroxyl radical has been detected in Chattonella cell suspension. By the physical stimulation, such as passing through between the gill lamellas of fish, the glycocalyx is easily discharged from the flagellate cells and attached on the gill surface, where ROS are continuously produced, which might cause gill tissue damage and fish death. Comparative studies using several strains of Chattonella showed that ROS production rate and ichthyotoxicity of Chattonella is well correlated. Furthermore, significant levels of ROS have been reported in other raphidophytes and dinoflagellates, such as Cochlodinium polykrikoides and Karenia mikimotoi. Chattonella is the most extensively studied phytoplankton in terms of ROS production and its biological functions. Therefore, this review examined the potential ecophysiological roles of extracellular ROS production by marine microalgae in aquatic environment.
Keywords: Chattonella; harmful algae bloom (HAB) species; marine microalgae; nitric oxide (NO); reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lauritano C., Andersen J.H., Hansen E., Albrigtsen M., Escalera L., Esposito F., Helland K., Hanssen K.Ø., Romano G., Ianora A. Bioactivity screening of microalgae for antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-diabetes, and antibacterial activities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016;3:68. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2016.00068. - DOI
-
- Landsberg J.H. The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2002;10:113–390. doi: 10.1080/20026491051695. - DOI
-
- Zohdi E., Abbaspour M. Harmful algal blooms (red tide): A review of causes, impacts and approaches to monitoring and prediction. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019;16:1789–1806. doi: 10.1007/s13762-018-2108-x. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources