Structure-Activity Relationships and Transcriptomic Analysis of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors
- PMID: 35204103
- PMCID: PMC8868400
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11020220
Structure-Activity Relationships and Transcriptomic Analysis of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors
Abstract
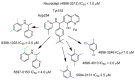
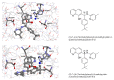
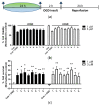
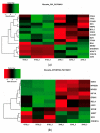
To evaluate the differences in action of commercially available 2-oxoglutarate mimetics and "branched-tail" oxyquinoline inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase (HIF PHD), the inhibitors' IC50 values in the activation of HIF1 ODD-luciferase reporter were selected for comparative transcriptomics. Structure-activity relationship and computer modeling for the oxyquinoline series of inhibitors led to the identification of novel inhibitors, which were an order of magnitude more active in the reporter assay than roxadustat and vadadustat. Unexpectedly, 2-methyl-substitution in the oxyquinoline core of the best HIF PHD inhibitor was found to be active in the reporter assay and almost equally effective in the pretreatment paradigm of the oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro model. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the signaling pathways induced by HIF PHD inhibitors showed high potency of the two novel oxyquinoline inhibitors (#4896-3249 and #5704-0720) at 2 μM concentrations matching the effect of 30 μM roxadustat and 500 μM dimethyl oxalyl glycine in inducing HIF1 and HIF2-linked pathways. The two oxyquinoline inhibitors exerted the same activation of HIF-triggered glycolytic pathways but opposite effects on signaling pathways linked to alternative substrates of HIF PHD 1 and 3, such as p53, NF-κB, and ATF4. This finding can be interpreted as the specificity of the 2-methyl-substitute variant for HIF PHD2.
Keywords: 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase; adaptaquin; hypoxia; iron chelation; neuradapt; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective Effect of HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibition in an In Vitro Hypoxia Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jul 24;9(8):662. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080662. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722310 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationship for branched oxyquinoline HIF activators: Effect of modifications to phenylacetamide "tail".Biochimie. 2017 Feb;133:74-79. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.12.004. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28007502
-
HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors for COVID-19 Treatment: Pros and Cons.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 29;11:621054. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.621054. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33584306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in anaemia of chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis including 13,146 patients.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021 Aug;46(4):999-1009. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13385. Epub 2021 Feb 21. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021. PMID: 33615523
-
Recent Advances in Developing Inhibitors for Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylases and Their Therapeutic Implications.Molecules. 2015 Nov 19;20(11):20551-68. doi: 10.3390/molecules201119717. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26610437 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jaakkola P., Mole D.R., Tian Y.-M., Wilson M.I., Gielbert J., Gaskell S.J., von Kriegsheim A., Hebestreit H.F., Mukherji M., Schofield C.J., et al. Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel-Lindau Ubiquitylation Complex by O2-Regulated Prolyl Hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–472. doi: 10.1126/science.1059796. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang S., Guo J., Xie S., Chen J., Yu S., Yu Y. Efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor (HIF-PHI) on anemia in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021;53:1139–1147. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02671-z. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

