Oxidant/Antioxidant Status Is Impaired in Sepsis and Is Related to Anti-Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Innate Immunity Alterations
- PMID: 35204114
- PMCID: PMC8868413
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11020231
Oxidant/Antioxidant Status Is Impaired in Sepsis and Is Related to Anti-Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Innate Immunity Alterations
Abstract
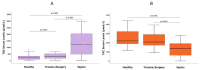
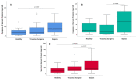
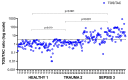
Oxidative stress is considered pivotal in the pathophysiology of sepsis. Oxidants modulate heat shock proteins (Hsp), interleukins (IL), and cell death pathways, including apoptosis. This multicenter prospective observational study was designed to ascertain whether an oxidant/antioxidant imbalance is an independent sepsis discriminator and mortality predictor in intensive care unit (ICU) patients with sepsis (n = 145), compared to non-infectious critically ill patients (n = 112) and healthy individuals (n = 89). Serum total oxidative status (TOS) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) were measured by photometric testing. IL-6, -8, -10, -27, Hsp72/90 (ELISA), and selected antioxidant biomolecules (Ζn, glutathione) were correlated with apoptotic mediators (caspase-3, capsase-9) and the central anti-apoptotic survivin protein (ELISA, real-time PCR). A wide scattering of TOS, TAC, and TOS/TAC in all three groups was demonstrated. Septic patients had an elevated TOS/TAC, compared to non-infectious critically ill patients and healthy individuals (p = 0.001). TOS/TAC was associated with severity scores, procalcitonin, IL-6, -10, -27, IFN-γ, Hsp72, Hsp90, survivin protein, and survivin isoforms -2B, -ΔΕx3, -WT (p < 0.001). In a propensity probability (age-sex-adjusted) logistic regression model, only sepsis was independently associated with TOS/TAC (Exp(B) 25.4, p < 0.001). The AUCTOS/TAC (0.96 (95% CI = 0.93-0.99)) was higher than AUCTAC (z = 20, p < 0.001) or AUCTOS (z = 3.1, p = 0.002) in distinguishing sepsis. TOS/TAC, TOS, survivin isoforms -WT and -2B, Hsp90, IL-6, survivin protein, and repressed TAC were strong predictors of mortality (p < 0.01). Oxidant/antioxidant status is impaired in septic compared to critically ill patients with trauma or surgery and is related to anti-apoptotic, inflammatory, and innate immunity alterations. The unpredicted TOS/TAC imbalance might be related to undefined phenotypes in patients and healthy individuals.
Keywords: TAC; TOS; antioxidant status; apoptosis; heat shock proteins; innate immunity; interleukins; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The value of serum total oxidant to the antioxidant ratio as a biomarker of knee osteoarthritis.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020 Aug;38:118-123. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.05.019. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020. PMID: 32690145
-
Evaluation of oxidative stress level: total antioxidant capacity, total oxidant status and glutathione activity in patients with COVID-19.New Microbes New Infect. 2021 Jul;42:100897. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100897. Epub 2021 May 17. New Microbes New Infect. 2021. PMID: 34026228 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Total Oxidant Status to the Antioxidant Capacity Ratio as a Valuable Biomarker in Breast Cancer Patients.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Jul;12(2):277-283. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.12.2.277. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38317813 Free PMC article.
-
Total antioxidant capacity and total oxidant status after surfactant treatment in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome.Ann Clin Biochem. 2011 Sep;48(Pt 5):462-7. doi: 10.1258/acb.2011.010285. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Ann Clin Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21775575
-
The Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Necroptotic Role of Zinc in COVID-19 and Sepsis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 31;12(11):1942. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111942. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of HSP27 in 28-day mortality in septic ICU patients: a retrospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 9;11:1513788. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1513788. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39850096 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Improves Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Septic Liver Injury by Inhibiting the Activation of ROCK/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Aug 4;13(8):e70757. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70757. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40766788 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Oral Ascorbic Acid Administration in Combination With IV N-acetylcysteine in Delaying Inflammatory Cascade in Sepsis: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Dec 3;15(12):e49868. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49868. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38169912 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency Electromagnetic and Pulsed Magnetic Fields Protected the Kidney Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Systemic Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis by Regulating the IL-6/HIF1α/eNOS and Bcl2/Bax/Cas-9 Pathways.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 29;61(2):238. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020238. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40005355 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of antioxidant supplementation on short-term mortality in sepsis patients.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 4;10(8):e29156. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29156. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38644822 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

