A Journey into the Clinical Relevance of Heme Oxygenase 1 for Human Inflammatory Disease and Viral Clearance: Why Does It Matter on the COVID-19 Scene?
- PMID: 35204159
- PMCID: PMC8868141
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11020276
A Journey into the Clinical Relevance of Heme Oxygenase 1 for Human Inflammatory Disease and Viral Clearance: Why Does It Matter on the COVID-19 Scene?
Abstract
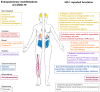
Heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), the rate-limiting enzyme in heme degradation, is involved in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis, exerting a cytoprotective role by its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory functions. HO-1 and its end products, biliverdin, carbon monoxide and free iron (Fe2+), confer cytoprotection against inflammatory and oxidative injury. Additionally, HO-1 exerts antiviral properties against a diverse range of viral infections by interfering with replication or activating the interferon (IFN) pathway. Severe cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), are characterized by systemic hyperinflammation, which, in some cases, leads to severe or fatal symptoms as a consequence of respiratory failure, lung and heart damage, kidney failure, and nervous system complications. This review summarizes the current research on the protective role of HO-1 in inflammatory diseases and against a wide range of viral infections, positioning HO-1 as an attractive target to ameliorate clinical manifestations during COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Dengue virus; Ebola virus; Hepatitis virus; SARS-CoV-2; Zika virus; heme oxygenase 1; human immunodeficiency virus; influenza A virus; respiratory syncytial virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

