Male Infertility and Oxidative Stress: A Focus on the Underlying Mechanisms
- PMID: 35204189
- PMCID: PMC8868102
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11020306
Male Infertility and Oxidative Stress: A Focus on the Underlying Mechanisms
Abstract
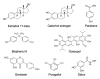
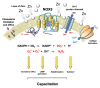
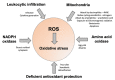
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a critical role in defining the functional competence of human spermatozoa. When generated in moderate amounts, ROS promote sperm capacitation by facilitating cholesterol efflux from the plasma membrane, enhancing cAMP generation, inducing cytoplasmic alkalinization, increasing intracellular calcium levels, and stimulating the protein phosphorylation events that drive the attainment of a capacitated state. However, when ROS generation is excessive and/or the antioxidant defences of the reproductive system are compromised, a state of oxidative stress may be induced that disrupts the fertilizing capacity of the spermatozoa and the structural integrity of their DNA. This article focusses on the sources of ROS within this system and examines the circumstances under which the adequacy of antioxidant protection might become a limiting factor. Seminal leukocyte contamination can contribute to oxidative stress in the ejaculate while, in the germ line, the dysregulation of electron transport in the sperm mitochondria, elevated NADPH oxidase activity, or the excessive stimulation of amino acid oxidase action are all potential contributors to oxidative stress. A knowledge of the mechanisms responsible for creating such stress within the human ejaculate is essential in order to develop better antioxidant strategies that avoid the unintentional creation of its reductive counterpart.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; amino acid oxidase; antioxidants; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; sperm mitochondria; spermatozoa.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have an association with CellOxess, a nutraceutical company engaged in the development and commercialization of antioxidant formulations for clinical use.
Figures
References
-
- Mason K.E. Testicular degeneration in albino rats fed a purified food ration. J. Exp. Zool. 1926;45:159–229. doi: 10.1002/jez.1400450106. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

