Protective Effect of Liposomal Epigallocatechin-Gallate in Experimental Gentamicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 35204293
- PMCID: PMC8869534
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11020412
Protective Effect of Liposomal Epigallocatechin-Gallate in Experimental Gentamicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
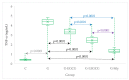
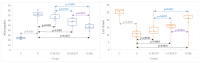
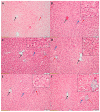
Our study aimed to assess the effect of liposomal epigallocatechin-gallate (LEGCG) compared with epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) solution on hepatic toxicity induced by gentamicin (G) administration in rats. Five groups were evaluated, a control group (no G administration) and four groups that received G (1 mL, i.p, 80 mg/kg b.w. (body weight/day), for 7 days) to which we associated daily administration 30 min before G of EGCG (G-EGCG, 2.5 mg/0.1 kg b.w.), LEGCG (G-LEGCG, 2.5 mg/0.1 kg b.w.) or silymarin (100 mg/kg b.w./day). The nitro-oxidative stress (NOx), catalase (CAT), TNF-α, transaminases, creatinine, urea, metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and 9, and liver histopathological changes were evaluated. LEGCG exhibited better efficacy than EGCG, improving the oxidant/antioxidant balance (p = 0.0125 for NOx and 0.0032 for CAT), TNF-α (p < 0.0001), MMP-2 (p < 0.0001), aminotransferases (p = 0.0001 for AST and 0.0136 for ALT), creatinine (p < 0.0001), urea (p = 0.0006) and histopathologic liver changes induced by gentamicin. Our study demonstrated the beneficial effect of EGCG with superior results of the liposomal formulation for hepatoprotection in experimental hepatic toxicity induced by gentamicin.
Keywords: epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG); gentamicin-induced hepatotoxicity; metalloproteinase (MMP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wong H.-S., Chen J.-H., Leong P.-K., Leung H.-Y., Chan W.-M., Ko K.-M. β-Sitosterol Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride Hepatotoxicity but not Gentamicin Nephrotoxicity in Rats via the Induction of Mitochondrial Glutathione Redox Cycling. Molecules. 2014;19:17649–17662. doi: 10.3390/molecules191117649. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bulboacă A.E., Porfire A., Bolboacă S.D., Nicula C.A., Feștilă D.G., Roman A., Râjnoveanu R.M., Râjnoveanu A., Dogaru G., Boarescu P.-M., et al. Protective Effects of Liposomal Curcumin on Oxidative Stress/Antioxidant Imbalance, Metalloproteinases 2 and -9, Histological Changes and Renal Function in Experimental Nephrotoxicity Induced by Gentamicin. Antioxidants. 2021;10:325. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020325. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali F.E.M., Hassanein E.H.M., Bakr A.G., El-Shoura E.A.M., El-Gamal D.A., Mahmoud A.R., Abd-Elhamid T.H. Ursodeoxycholic acid abrogates gentamicin-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: Role of NF-kappaB-p65/TNF-alpha, Bax/Bcl-xl/Caspase-3, and eNOS/iNOS pathways. Life Sci. 2020;254:117760. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117760. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arjinajarn P., Chueakula N., Pongchaidecha A., Jaikumkao K., Chatsudthipong V., Mahatheeranont S., Norkaew O., Chattipakorn N., Lungkaphin A. Anthocyanin-rich Riceberry bran extract attenuates gentamicin-inducedhepatotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;92:412–420. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.100. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

