Deep Learning Approach to Automatize TMTV Calculations Regardless of Segmentation Methodology for Major FDG-Avid Lymphomas
- PMID: 35204515
- PMCID: PMC8870809
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12020417
Deep Learning Approach to Automatize TMTV Calculations Regardless of Segmentation Methodology for Major FDG-Avid Lymphomas
Abstract
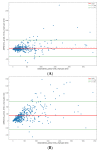
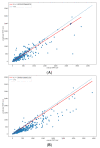
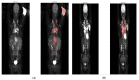
The total metabolic tumor volume (TMTV) is a new prognostic factor in lymphomas that could benefit from automation with deep learning convolutional neural networks (CNN). Manual TMTV segmentations of 1218 baseline 18FDG-PET/CT have been used for training. A 3D V-NET model has been trained to generate segmentations with soft dice loss. Ground truth segmentation has been generated using a combination of different thresholds (TMTVprob), applied to the manual region of interest (Otsu, relative 41% and SUV 2.5 and 4 cutoffs). In total, 407 and 405 PET/CT were used for test and validation datasets, respectively. The training was completed in 93 h. In comparison with the TMTVprob, mean dice reached 0.84 in the training set, 0.84 in the validation set and 0.76 in the test set. The median dice scores for each TMTV methodology were 0.77, 0.70 and 0.90 for 41%, 2.5 and 4 cutoff, respectively. Differences in the median TMTV between manual and predicted TMTV were 32, 147 and 5 mL. Spearman's correlations between manual and predicted TMTV were 0.92, 0.95 and 0.98. This generic deep learning model to compute TMTV in lymphomas can drastically reduce computation time of TMTV.
Keywords: convolutional neural network; deep learning; lymphoma; total metabolic tumor volume.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Cottereau A.-S., Versari A., Loft A., Casasnovas O., Bellei M., Ricci R., Bardet S., Castagnoli A., Brice P., Raemaekers J., et al. Prognostic Value of Baseline Metabolic Tumor Volume in Early-Stage Hodgkin Lymphoma in the Standard Arm of the H10 Trial. Blood. 2018;131:1456–1463. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-07-795476. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kanoun S., Rossi C., Berriolo-Riedinger A., Dygai-Cochet I., Cochet A., Humbert O., Toubeau M., Ferrant E., Brunotte F., Casasnovas R.-O. Baseline Metabolic Tumour Volume Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2014;41:1735–1743. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2783-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thieblemont C., Howlett S., Casasnovas R.-O., Mounier N., Perrot A., Morschhauser F., Fruchart C., Daguindau N., van Eygen K., Obéric L., et al. Lenalidomide Maintenance for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients Responding to R-CHOP: Quality of Life, Dosing, and Safety Results from the Randomised Controlled REMARC Study. Br. J. Haematol. 2020;189:84–96. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16300. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meignan M., Cottereau A.S., Versari A., Chartier L., Dupuis J., Boussetta S., Grassi I., Casasnovas R.-O., Haioun C., Tilly H., et al. Baseline Metabolic Tumor Volume Predicts Outcome in High–Tumor-Burden Follicular Lymphoma: A Pooled Analysis of Three Multicenter Studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016;34:3618–3626. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.9440. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grossiord E., Passat N., Talbot H., Naegel B., Kanoun S., Tal I., Tervé P., Ken S., Casasnovas O., Meignan M., et al. Shaping for PET Image Analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020;131:307–313. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2020.01.017. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

