Machine Learning-Based Modeling of Ovarian Response and the Quantitative Evaluation of Comprehensive Impact Features
- PMID: 35204580
- PMCID: PMC8871024
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12020492
Machine Learning-Based Modeling of Ovarian Response and the Quantitative Evaluation of Comprehensive Impact Features
Abstract
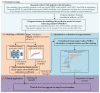
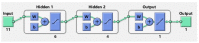
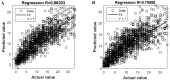
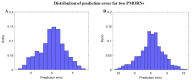
Appropriate ovarian responses to the controlled ovarian stimulation strategy is the premise for a good outcome of the in vitro fertilization cycle. With the booming of artificial intelligence, machine learning is becoming a popular and promising approach for tailoring a controlled ovarian stimulation strategy. Nowadays, most machine learning-based tailoring strategies aim to generally classify the controlled ovarian stimulation outcome, lacking the capacity to precisely predict the outcome and evaluate the impact features. Based on a clinical cohort composed of 1365 women and two machine learning methods of artificial neural network and supporting vector regression, a regression prediction model of the number of oocytes retrieved is trained, validated, and selected. Given the proposed model, an index called the normalized mean impact value is defined and calculated to reflect the importance of each impact feature. The proposed models can estimate the number of oocytes retrieved with high precision, with the regression coefficient being 0.882% and 89.84% of the instances having the prediction number ≤ 5. Among the impact features, the antral follicle count has the highest importance, followed by the E2 level on the human chorionic gonadotropin day, the age, and the Anti-Müllerian hormone, with their normalized mean impact value > 0.3. Based on the proposed model, the prognostic results for ovarian response can be predicted, which enables scientific clinical decision support for the customized controlled ovarian stimulation strategies for women, and eventually helps yield better in vitro fertilization outcomes.
Keywords: clinical decision support; controlled ovarian stimulation; dosage of Gn; machine learning; number of oocytes retrieved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Van Montfoort A.P.A., Arts E., Wijnandts L., Sluijmer A., Pelinck M.J., Land J.A., Van Echten-Arends J. Reduced oxygen concentration during human IVF culture improves embryo utilization and cumulative pregnancy rates per cycle. Hum. Reprod. Open. 2020;2020:hoz036. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoz036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li H.W.R., Lee V.C.Y., Lau E.Y.L., Yeung W.S.B., Ho P.C., Ng E. Role of Baseline Antral Follicle Count and Anti-Mullerian Hormone in Prediction of Cumulative Live Birth in the First In Vitro Fertilisation Cycle: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e61095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

