Evaluation of a Generative Adversarial Network to Improve Image Quality and Reduce Radiation-Dose during Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
- PMID: 35204582
- PMCID: PMC8871529
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12020495
Evaluation of a Generative Adversarial Network to Improve Image Quality and Reduce Radiation-Dose during Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
Abstract
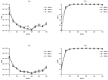
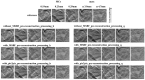
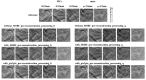
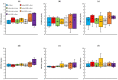
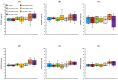
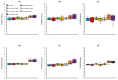
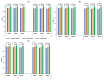
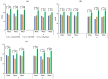
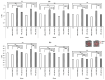
In this study, we evaluated the improvement of image quality in digital breast tomosynthesis under low-radiation dose conditions of pre-reconstruction processing using conditional generative adversarial networks [cGAN (pix2pix)]. Pix2pix pre-reconstruction processing with filtered back projection (FBP) was compared with and without multiscale bilateral filtering (MSBF) during pre-reconstruction processing. Noise reduction and preserve contrast rates were compared using full width at half-maximum (FWHM), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), and structural similarity (SSIM) in the in-focus plane using a BR3D phantom at various radiation doses [reference-dose (automatic exposure control reference dose: AECrd), 50% and 75% reduction of AECrd] and phantom thicknesses (40 mm, 50 mm, and 60 mm). The overall performance of pix2pix pre-reconstruction processing was effective in terms of FWHM, PSNR, and SSIM. At ~50% radiation-dose reduction, FWHM yielded good results independently of the microcalcification size used in the BR3D phantom, and good noise reduction and preserved contrast. PSNR results showed that pix2pix pre-reconstruction processing represented the minimum in the error with reference FBP images at an approximately 50% reduction in radiation-dose. SSIM analysis indicated that pix2pix pre-reconstruction processing yielded superior similarity when compared with and without MSBF pre-reconstruction processing at ~50% radiation-dose reduction, with features most similar to the reference FBP images. Thus, pix2pix pre-reconstruction processing is promising for reducing noise with preserve contrast and radiation-dose reduction in clinical practice.
Keywords: digital breast tomosynthesis; generative adversarial networks; improve image quality; radiation-dose reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Skaane P., Bandos A.I., Gullien R., Eben E.B., Ekseth U., Haakenaasen U., Izadi M., Jebsen I.N., Jahr G., Krager M., et al. Comparison of digital mammography alone and digital mammography plus tomosynthesis in a population-based screening program. Radiology. 2013;267:47–56. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12121373. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Helvie M.A., Roubidoux M.A., Zhang Y., Carson P.L., Chan H.P. Tomosynthesis mammography vs conventional mammography: Lesion detection and reader reference. Initial experience; Proceedings of the Radiological Society of North America 92nd Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting; Chicago, IL, USA. 26 November–1 December 2003; p. 335.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

