Diagnostic Performance of Point Shear Wave Elastography (pSWE) Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Technology in Mesenteric Masses: A Feasibility Study
- PMID: 35204612
- PMCID: PMC8870845
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12020523
Diagnostic Performance of Point Shear Wave Elastography (pSWE) Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Technology in Mesenteric Masses: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic performance of ultrasound point shear wave elastography (pSWE) using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) technology in different benign and malignant mesenteric masses (MMs).
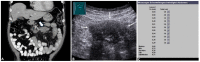
Methods: A total of 69 patients with MMs diagnosed from September 2018 to November 2021 were included retrospectively in the study. The inclusion criteria were (1) an MM over 1 cm; (2) valid ARFI measurements; and (3) confirmation of the diagnosis of an MM by histological examination and/or clinical and radiological follow-up. To examine the mean ARFI velocities (MAVs) for potential cut-off values between benign and malignant MMs, a receiver operating characteristics analysis was implemented.
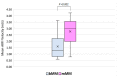
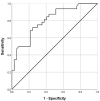
Results: In total, 37/69 of the MMs were benign (53.6%) and 32/69 malignant (46.4%). Benign MMs demonstrated significantly lower MAVs than mMMs (1.59 ± 0.93 vs. 2.76 ± 1.01 m/s; p < 0.001). Selecting 2.05 m/s as a cut-off value yielded a sensitivity and specificity of 75.0% and 70.3%, respectively, in diagnosing malignant MMs (area under the curve = 0.802, 95% confidence interval 0.699-0.904).
Conclusion: ARFI elastography may represent an additional non-invasive tool for differentiating benign from malignant MMs. However, to validate the results of this study, further prospective randomized studies are required.
Keywords: ARFI elastography; mesenteric mass; mesentery; sclerosing mesenteritis; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ARFI elastography of the omentum: feasibility and diagnostic performance in differentiating benign from malignant omental masses.BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022 May;9(1):e000901. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2022-000901. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35523459 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Point Shear Wave Elastography Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Technology in Peripheral Pulmonary Consolidations: A Feasibility Study.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2022 May;48(5):778-785. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2021.12.015. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35151527
-
Characterization of focal liver masses using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan 14;19(2):219-26. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.219. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23345944 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Shear Wave Velocity Measurement on Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Differential Diagnosis between Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: A Meta-analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015 Dec;41(12):3035-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26371402 Review.
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for differentiation of malignant and benign breast lesions: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):4753-61. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Elastography of Focal Splenic Lesions: Feasibility and Diagnostic Potential.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;15(20):4964. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204964. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894331 Free PMC article.
-
ARFI elastography of the omentum: feasibility and diagnostic performance in differentiating benign from malignant omental masses.BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022 May;9(1):e000901. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2022-000901. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35523459 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating Benign from Malignant Causes of Splenomegaly: Is Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography Helpful?Diseases. 2024 Nov 30;12(12):308. doi: 10.3390/diseases12120308. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 39727638 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

