A Rare Case of Hepatic Vanishing Bile Duct Syndrome Occurring after Combination Therapy with Nivolumab and Cabozantinib in a Patient with Renal Carcinoma
- PMID: 35204627
- PMCID: PMC8871391
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12020539
A Rare Case of Hepatic Vanishing Bile Duct Syndrome Occurring after Combination Therapy with Nivolumab and Cabozantinib in a Patient with Renal Carcinoma
Abstract
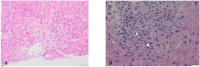
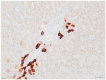
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) significantly improve the outcomes of patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); however, high-grade toxicities can occur, particularly during combination therapy. Herein, we report a patient with advanced metastatic ccRCC, who developed grade 4 cholestasis during combined therapy with nivolumab and cabozantinib. After the exclusion of common disorders associated with cholestasis and a failure of corticosteroids (CS), a liver biopsy was performed that demonstrated severe ductopenia. Consequently, a diagnosis of vanishing bile duct syndrome related to TKI and ICI administration was made, resulting in CS discontinuation and ursodeoxycholic acid administration. After a 7-month follow-up, liver tests had returned to normal values. Immunological studies revealed that our patient had developed robust T-cells and macrophages infiltrates in his lung metastasis, as well as in skin and liver tissues at the onset of toxicities. At the same time, peripheral blood immunophenotyping revealed significant changes in T-cell subsets, suggesting their potential role in the pathophysiology of the disease.
Keywords: checkpoint inhibitors; cholestasis; immune related adverse events; severe ductopenia; vanishing bile duct syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Choueiri T.K., Halabi S., Sanford B.L., Hahn O., Michaelson M.D., Walsh M.K., Feldman D.R., Olencki T., Picus J., Small E.J., et al. Cabozantinib Versus Sunitinib As Initial Targeted Therapy for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma of Poor or Intermediate Risk: The Alliance A031203 CABOSUN Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:591–597. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.7398. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choueiri T.K., Hessel C., Halabi S., Sanford B., Michaelson M.D., Hahn O., Walsh M., Olencki T., Picus J., Small E.J., et al. Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma of intermediate or poor risk (Alliance A031203 CABOSUN randomised trial): Progression-free survival by independent review and overall survival update. Eur. J. Cancer. 2018;94:115–125. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.02.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rini B.I., Battle D., Figlin R.A., George D.J., Hammers H., Hutson T., Jonasch E., Joseph R.W., McDermott D.F., Motzer R.J., et al. The society for immunotherapy of cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) J. Immunother. Cancer. 2019;7:354. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0813-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

