Systemic Treatment with Pioglitazone Reverses Vision Loss in Preclinical Glaucoma Models
- PMID: 35204782
- PMCID: PMC8961625
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12020281
Systemic Treatment with Pioglitazone Reverses Vision Loss in Preclinical Glaucoma Models
Abstract
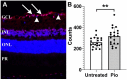
Neuroinflammation significantly contributes to the pathophysiology of several neurodegenerative diseases. This is also the case in glaucoma and may be a reason why many patients suffer from progressive vision loss despite maximal reduction in intraocular pressure. Pioglitazone is an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) whose pleiotrophic activities include modulation of cellular energy metabolism and reduction in inflammation. In this study we employed the DBA2/J mouse model of glaucoma with chronically elevated intraocular pressure to investigate whether oral low-dose pioglitazone treatment preserves retinal ganglion cell (RGC) survival. We then used an inducible glaucoma model in C57BL/6J mice to determine visual function, pattern electroretinographs, and tracking of optokinetic reflex. Our findings demonstrate that pioglitazone treatment does significantly protect RGCs and prevents axonal degeneration in the glaucomatous retina. Furthermore, treatment preserves and partially reverses vision loss in spite of continuously elevated intraocular pressure. These data suggest that pioglitazone may provide treatment benefits for those glaucoma patients experiencing continued vision loss.
Keywords: PPARγ; glaucoma; glucose metabolism; pioglitazone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Gharahkhani P., Jorgenson E., Hysi P., Khawaja A.P., Pendergrass S., Han X., Ong J.S., Hewitt A.W., Segre A.V., Rouhana J.M., et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 127 open-angle glaucoma loci with consistent effect across ancestries. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:1258. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20851-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

