Quantitative Real-Time Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in Peripheral Blood Samples of Hypertension Patients
- PMID: 35205232
- PMCID: PMC8872078
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13020187
Quantitative Real-Time Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in Peripheral Blood Samples of Hypertension Patients
Abstract
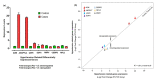
Hypertension (HTN) is considered one of the most important and well-established reasons for cardiovascular abnormalities, strokes, and premature mortality globally. This study was designed to explore possible differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that contribute to the pathophysiology of hypertension. To identify the DEGs of HTN, we investigated 22 publicly available cDNA Affymetrix datasets using an integrated system-level framework. Gene Ontology (GO), pathway enrichment, and transcriptional factors were analyzed to reveal biological information. From 50 DEGs, we ranked 7 hypertension-related genes (p-value < 0.05): ADM, ANGPTL4, USP8, EDN, NFIL3, MSR1, and CEBPD. The enriched terms revealed significant functional roles of HIF-1-α transcription; endothelin; GPCR-binding ligand; and signaling pathways of EGF, PIk3, and ARF6. SP1 (66.7%), KLF7 (33.3%), and STAT1 (16.7%) are transcriptional factors associated with the regulatory mechanism. The expression profiles of these DEGs as verified by qPCR showed 3-times higher fold changes (2-ΔΔCt) in ADM, ANGPTL4, USP8, and EDN1 genes compared to control, while CEBPD, MSR1 and NFIL3 were downregulated. The aberrant expression of these genes is associated with the pathophysiological development and cardiovascular abnormalities. This study will help to modulate the therapeutic strategies of hypertension.
Keywords: cDNA datasets; differentially expressed genes; enrichment analysis; expression profiling; hypertension; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ishtiaq S., Ilyas U., Naz S., Altaf R., Afzaal H., Muhammad S.A., uz Zaman S., Imran M., Ali F., Sohail F. Assessment of the risk factors of hypertension among adult & elderly group in twin cities of Pakistan. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2017;67:1664–1669. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

