LiKidMiRs: A ddPCR-Based Panel of 4 Circulating miRNAs for Detection of Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 35205607
- PMCID: PMC8869982
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14040858
LiKidMiRs: A ddPCR-Based Panel of 4 Circulating miRNAs for Detection of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Decreased renal cell cancer-related mortality is an important societal goal, embodied by efforts to develop effective biomarkers enabling early detection and increasing the likelihood of curative treatment. Herein, we sought to develop a new biomarker for early and minimally invasive detection of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) based on a microRNA panel assessed by ddPCR.
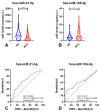
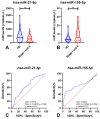
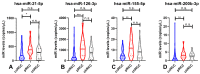
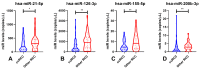
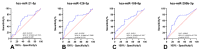
Methods: Plasma samples from patients with RCC (n = 124) or oncocytomas (n = 15), and 64 healthy donors, were selected. Hsa-miR-21-5p, hsa-miR-126-3p, hsa-miR-155-5p and hsa-miR-200b-3p levels were evaluated using a ddPCR protocol.
Results: RCC patients disclosed significantly higher circulating levels of hsa-miR-155-5p compared to healthy donors, whereas the opposite was observed for hsa-miR-21-5p levels. Furthermore, hsa-miR-21-5p and hsa-miR-155-5p panels detected RCC with high sensitivity (82.66%) and accuracy (71.89%). The hsa-miR-126-3p/hsa-miR-200b-3p panel identified the most common RCC subtype (clear cell, ccRCC) with 74.78% sensitivity.
Conclusion: Variable combinations of plasma miR levels assessed by ddPCR enable accurate detection of RCC in general, and of ccRCC. These findings, if confirmed in larger studies, provide evidence for a novel ancillary tool which might aid in early detection of RCC.
Keywords: circulating miRNA; ddPCR; diagnosis; malignancy; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shuch B., Amin A., Armstrong A.J., Eble J.N., Ficarra V., Lopez-Beltran A., Martignoni G., Rini B.I., Kutikov A. Understanding pathologic variants of renal cell carcinoma: Distilling therapeutic opportunities from biologic complexity. Eur. Urol. 2015;67:85–97. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.04.029. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

