Mental Health and Quality of Life among Patients with Cancer during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: Results from the Longitudinal ONCOVID Survey Study
- PMID: 35205838
- PMCID: PMC8869927
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14041093
Mental Health and Quality of Life among Patients with Cancer during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: Results from the Longitudinal ONCOVID Survey Study
Abstract
Purpose: This longitudinal survey study aimed to investigate the self-reported outcome measures of COVID-19 peritraumatic distress, depression, anxiety, stress, quality of life (QOL), and their associated factors in a cohort of cancer patients treated at a tertiary care hospital during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
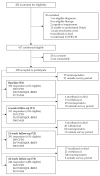
Methods: Surveys were administered at four time points between 1 April 2020 and 18 September 2020. The surveys included the CPDI, DASS-21, and WHOQOL-BREF questionnaires.
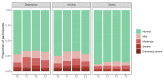
Results: Survey response rates were high (61.0% to 79.1%). Among the 355 participants, 71.3% were female, and the median age was 62.2 years (IQR, 53.9 to 69.1). The majority (78.6%) were treated with palliative intention. An important proportion of the participants reported symptoms of COVID-19 peritraumatic distress (34.2% to 39.6%), depression (27.6% to 33.5%), anxiety (24.9% to 32.7%), and stress (11.4% to 15.7%) at any time point during the study period. We did not find clinically meaningful mental health and QOL differences during the study period, with remarkably little change in between the pandemic's first and second wave. We found no consistent correlates of mental health or QOL scores, including cancer type, therapy intention, and sociodemographic information.
Conclusion: This cohort of cancer patients showed considerable resilience against mental health and QOL deterioration during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; cancer; coronavirus 2019; mental health; pandemic; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no personal disclosures. The Department of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Medical Oncology (Ghent University Hospital) reports non-financial support (congress and travel support) from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Eli Lilly and Company, GSK, Incyte, Pfizer, PharmaMar, MSD, Novartis, Nutrisan, Roche, Sanofi, Tesaro, and Teva, and grants from MSD and Roche, all outside the submitted work and associated institutions. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 4 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

