Adverse Perinatal Outcomes in COVID-19 Infected Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35206820
- PMCID: PMC8871986
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10020203
Adverse Perinatal Outcomes in COVID-19 Infected Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
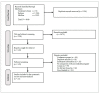
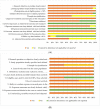
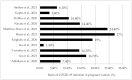
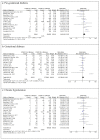
The impact of COVID-19 virus infection during pregnancy is still unclear. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to quantitatively pool the evidence on impact of COVID-19 infection on perinatal outcomes. Databases of Medline, Embase, and Cochrane library were searched using the keywords related to COVID-19 and perinatal outcomes from December 2019 to 30 June 2021. Observational studies comparing the perinatal outcomes of COVID-19 infection in pregnancy with a non-infected comparator were included. The screening process and quality assessment of the included studies were performed independently by two reviewers. Meta-analyses were used to pool the comparative dichotomous data on perinatal outcomes. The database search yielded 4049 results, 1254 of which were duplicates. We included a total of 21 observational studies that assessed the adverse perinatal outcomes with COVID-19 infection. The odds of maternal death (pooled OR: 7.05 [2.41-20.65]), preeclampsia (pooled OR: 1.39 [1.29-1.50]), cesarean delivery (pooled OR: 1.67 [1.29-2.15]), fetal distress (pooled OR: 1.66 [1.35-2.05]), preterm birth (pooled OR: 1.86 [1.34-2.58]), low birth weight (pooled OR: 1.69 [1.35-2.11]), stillbirth (pooled OR: 1.46 [1.16-1.85]), 5th minute Apgar score of less than 7 (pooled OR: 1.44 [1.11-1.86]) and admissions to neonatal intensive care unit (pooled OR: 2.12 [1.36-3.32]) were higher among COVID-19 infected pregnant women compared to non-infected pregnant women.
Keywords: COVID-19; perinatal outcomes; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- World Health Organization Situation Report—85: Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) 2020. [(accessed on 5 October 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/situation-report---85.
-
- Peeri N.C., Shrestha N., Rahman M.S., Zaki R., Tan Z., Bibi S., Baghbanzadeh M., Aghamohammadi N., Zhang W., Haque U. The SARS, MERS and novel coronavirus (COVID-19) epidemics, the newest and biggest global health threats: What lessons have we learned? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020;49:717–726. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyaa033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2021. [(accessed on 4 December 2021)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

