Lipid Biomarkers in Depression: Does Antidepressant Therapy Have an Impact?
- PMID: 35206947
- PMCID: PMC8872589
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10020333
Lipid Biomarkers in Depression: Does Antidepressant Therapy Have an Impact?
Abstract
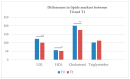
Studies have revealed mixed results on how antidepressant drugs affect lipid profiles of patients with major depression disorder (MDD). Even less is known about how patients respond to a switch of antidepressant medication with respect to their metabolic profile. For this, effects of a switch in antidepressants medication on lipid markers were studied in MDD patients. 15 participants (females = 86.67%; males = 13.33%; age: 49.45 ± 7.45 years) with MDD and a prescribed switch in their antidepressant medication were recruited at a psychosomatic rehabilitation clinic. Participants were characterized (with questionnaires and blood samples) at admission to the rehabilitation clinic (baseline, T0) and followed up with a blood sample two weeks (T1) later. HDL, LDL, total cholesterol, and triglycerides were determined (T0), and their change analyzed (Wilcoxon test) at follow up (T1). Decrements in HDL (p = 0.041), LDL (p < 0.001), and total cholesterol (p < 0.001) were observed two weeks after a switch in antidepressant medication. Triglycerides showed no difference (p = 0.699). Overall, LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol are affected by a change in antidepressant drugs in patients with MDD. These observations are of clinical relevance for medical practitioners in the planning and management of treatment strategies for MDD patients.
Keywords: HDL; LDL; antidepressants; cholesterol; high density lipoprotein cholesterol; lipids; low density lipoprotein cholesterol; major depressive disorder; triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Depression. [(accessed on 10 September 2021)];2020 Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/de-tail/depression.
-
- Maske U.E., Buttery A.K., Beesdo-Baum K., Riedel-Heller S., Hapke U., Busch M.A. Prevalence and correlates of DSM-IV-TR major depressive disorder, self-reported diagnosed depression and current depressive symptoms among adults in Germany. J. Affect. Disord. 2016;190:167–177. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.10.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- König H., Rommel A., Thom J., Schmidt C., König H.-H., Brettschneider C., Konnopka A. The excess costs of depression and the influence of sociodemographic and socioeconomic factors: Results from the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS) Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39:667–680. doi: 10.1007/s40273-021-01000-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

