The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Burnout, Compassion Fatigue, and Compassion Satisfaction in Healthcare Personnel: A Systematic Review of the Literature Published during the First Year of the Pandemic
- PMID: 35206978
- PMCID: PMC8872521
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10020364
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Burnout, Compassion Fatigue, and Compassion Satisfaction in Healthcare Personnel: A Systematic Review of the Literature Published during the First Year of the Pandemic
Abstract
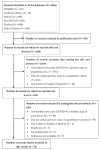
This literature review aimed to determine the level of burnout, compassion fatigue, and compassion satisfaction, as well as their associated risks and protective factors, in healthcare professionals during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. We reviewed 2858 records obtained from the CINAHL, Cochrane Library, Embase, PsycINFO, PubMed, and Web of Science databases, and finally included 76 in this review. The main results we found showed an increase in the rate of burnout, dimensions of emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and compassion fatigue; a reduction in personal accomplishment; and levels of compassion satisfaction similar to those before the pandemic. The main risk factors associated with burnout were anxiety, depression, and insomnia, along with some sociodemographic variables such as being a woman or a nurse or working directly with COVID-19 patients. Comparable results were found for compassion fatigue, but information regarding compassion satisfaction was lacking. The main protective factors were resilience and social support.
Keywords: COVID-19; burnout; compassion fatigue; compassion satisfaction; health personnel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Galli F., Pozzi G., Ruggiero F., Mameli F., Cavicchioli M., Barbieri S., Canevini M.P., Priori A., Pravettoni G., Sani G., et al. A Systematic Review and Provisional Metanalysis on Psychopathologic Burden on Health Care Workers of Coronavirus Outbreaks. Front. Psychiatry. 2020;11:568664. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.568664. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cai H., Tu B., Ma J., Chen L., Fu L., Jiang Y., Zhuang Q. Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies of Frontline Medical Staff in Hunan between January and March 2020 during the Outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Hubei, China. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020;26:e924171. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924171. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources