Temporal Change in Renoprotective Effect of Tolvaptan on Patients with Heart Failure: AURORA Study
- PMID: 35207249
- PMCID: PMC8879381
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11040977
Temporal Change in Renoprotective Effect of Tolvaptan on Patients with Heart Failure: AURORA Study
Abstract
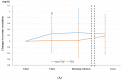
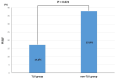
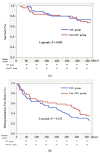
(1) Background: It has been reported that tolvaptan (TLV) has a renoprotective effect in acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) patients, but whether this effect is continued for a long time is unclear. Thus, we evaluated the time course of the renoprotective effect of TLV, in addition to the prognosis, in ADHF patients. (2) Methods: We investigated 911 ADHF patients from the AURORA (Acute Heart Failure Registry in Osaka Rosai Hospital) registry. After propensity score matching, 58 patients who started to receive TLV at least two days after the hospitalization (TLV group) and 58 who did not (non-TLV group) were examined. We compared the changes in the creatinine (Cr) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) between baseline and each time point (five days, discharge, and one year) as the index of the renoprotective effect, and rate of rehospitalizations and all-cause mortality for one year between the two groups. (3) Results: The change in Cr and eGFR levels was significantly higher in the TLV group than the non-TLV group five days after admission but the difference between the two groups gradually diminished. A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the survival and rehospitalization rates in the TLV and non-TLV groups were similar up to one year. (4) TLV revealed a temporal change in the renoprotective effect, which may be correlated with no long-term beneficial effect of TLV.
Keywords: diuretics; heart failure; renal function; tolvaptan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suitable Dose of Long-Term Tolvaptan to Reduce Heart Failure Rehospitalizations.Int Heart J. 2022;63(1):85-90. doi: 10.1536/ihj.21-396. Int Heart J. 2022. PMID: 35095082
-
Clinical benefit of tolvaptan in patients with acute decompensated heart failure and chronic kidney disease.Heart Vessels. 2016 Oct;31(10):1643-9. doi: 10.1007/s00380-015-0775-9. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Heart Vessels. 2016. PMID: 26615607
-
The effects of tolvaptan dose on cardiac mortality in patients with acute decompensated heart failure after hospital discharge.Heart Vessels. 2018 Oct;33(10):1204-1213. doi: 10.1007/s00380-018-1177-6. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Heart Vessels. 2018. PMID: 29687159
-
Tolvaptan Improves Prognosis in Responders with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure by Reducing the Dose of Loop Diuretics.Int Heart J. 2018;59(1):87-93. doi: 10.1536/ihj.17-099. Int Heart J. 2018. PMID: 29375117
-
Hemodynamic and Hormonal Effects of Tolvaptan for Heart Failure.Intern Med. 2019 Feb 15;58(4):471-475. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1697-18. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30210135 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goh C.Y., Vizzi G., De Cal M., Ronco C. Cardiorenal syndrome: A complex series of combined heart/kidney disorders. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011;174:33–45. - PubMed
-
- Tamaki S., Sato Y., Yamada T., Morita T., Furukawa Y., Iwasaki Y., Kawasaki M., Kikuchi A., Kondo T., Ozaki T., et al. Tolvaptan Reduces the Risk of Worsening Renal Function in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure and Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction—Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. Circ. J. 2017;81:740–747. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-16-1122. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

