The Utility of Genomic Testing for Hyperphenylalaninemia
- PMID: 35207333
- PMCID: PMC8879487
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11041061
The Utility of Genomic Testing for Hyperphenylalaninemia
Abstract
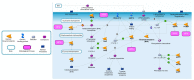
Hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA), the most common amino acid metabolism disorder, is caused by defects in enzymes involved in phenylalanine metabolism, with the consequent accumulation of phenylalanine and its secondary metabolites in body fluids and tissues. Clinical manifestations of HPA include mental retardation, and its early diagnosis with timely treatment can improve the prognosis of affected patients. Due to the genetic complexity and heterogeneity of HPA, high-throughput molecular technologies, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), are becoming indispensable tools to fully characterize the etiology, helping clinicians to promptly identify the exact patients' genotype and determine the appropriate treatment. In this review, after a brief overview of the key enzymes involved in phenylalanine metabolism, we represent the wide spectrum of genes and their variants associated with HPA and discuss the utility of genomic testing for improved diagnosis and clinical management of HPA.
Keywords: genomics; hyperphenylalaninemia; inherited metabolic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Levy H., Lamppu D., Anastosoaie V., Baker J.L., DiBona K., Hawthorne S., Lindenberger J., Kinch D., Seymour A., McIlduff M., et al. 5-year retrospective analysis of patients with phenylketonuria (PKU) and hyperphenylalaninemia treated at two specialized clinics. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020;129:177–185. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.12.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

