Bacillus mycoides PM35 Reinforces Photosynthetic Efficiency, Antioxidant Defense, Expression of Stress-Responsive Genes, and Ameliorates the Effects of Salinity Stress in Maize
- PMID: 35207506
- PMCID: PMC8875943
- DOI: 10.3390/life12020219
Bacillus mycoides PM35 Reinforces Photosynthetic Efficiency, Antioxidant Defense, Expression of Stress-Responsive Genes, and Ameliorates the Effects of Salinity Stress in Maize
Abstract
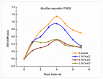
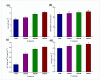
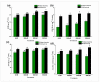
Soil salinity is one of the abiotic constraints that imbalance nutrient acquisition, hampers plant growth, and leads to potential loss in agricultural productivity. Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) can alleviate the adverse impacts of salt stress by mediating molecular, biochemical, and physiological status. In the present study, the bacterium Bacillus mycoides PM35 showed resistance up to 3 M NaCl stress and exhibited plant growth-promoting features. Under salinity stress, the halo-tolerant bacterium B. mycoides PM35 showed significant plant growth-promoting traits, such as the production of indole acetic acid, siderophore, ACC deaminase, and exopolysaccharides. Inoculation of B. mycoides PM35 alleviated salt stress in plants and enhanced shoot and root length under salinity stress (0, 300, 600, and 900 mM). The B. mycoides PM35 alleviated salinity stress by enhancing the photosynthetic pigments, carotenoids, radical scavenging capacity, soluble sugars, and protein content in inoculated maize plants compared to non-inoculated plants. In addition, B. mycoides PM35 significantly boosted antioxidant activities, relative water content, flavonoid, phenolic content, and osmolytes while reducing electrolyte leakage, H2O2, and MDA in maize compared to control plants. Genes conferring abiotic stress tolerance (CzcD, sfp, and srfAA genes) were amplified in B. mycoides PM35. Moreover, all reactions are accompanied by the upregulation of stress-related genes (APX and SOD). Our study reveals that B. mycoides PM35 is capable of promoting plant growth and increasing agricultural productivity.
Keywords: abiotic stress; bio-surfactant; plant growth-promoting bacteria; plant–microbe interactions; salinity stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Giménez A., Martínez-Ballesta M.D.C., Egea-Gilabert C., Gómez P.A., Artés-Hernández F., Pennisi G., Orsini F., Crepaldi A., Fernández J.A. Combined effect of salinity and LED lights on the yield and quality of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) microgreens. Horticulturae. 2021;7:180. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7070180. - DOI
-
- Syed A., Sarwar G., Shah S.H., Muhammad S. Soil salinity research in 21st century in Pakistan: Its impact on availability of plant nutrients, growth and yield of crops. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2021;52:183–200. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2020.1854294. - DOI
-
- Cheng Z., Woody O.Z., McConkey B.J., Glick B.R. Combined effects of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Pseudomonas putida UW4 and salinity stress on the Brassica napus proteome. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012;61:255–263. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.10.006. - DOI
-
- Nachshon U. Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: Trends, processes and examples. Water. 2018;10:1030.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

