COVID-19 Detection in CT/X-ray Imagery Using Vision Transformers
- PMID: 35207797
- PMCID: PMC8876295
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12020310
COVID-19 Detection in CT/X-ray Imagery Using Vision Transformers
Abstract
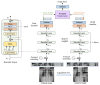
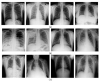
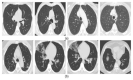
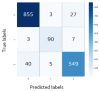
The steady spread of the 2019 Coronavirus disease has brought about human and economic losses, imposing a new lifestyle across the world. On this point, medical imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) and X-ray have demonstrated a sound screening potential. Deep learning methodologies have evidenced superior image analysis capabilities with respect to prior handcrafted counterparts. In this paper, we propose a novel deep learning framework for Coronavirus detection using CT and X-ray images. In particular, a Vision Transformer architecture is adopted as a backbone in the proposed network, in which a Siamese encoder is utilized. The latter is composed of two branches: one for processing the original image and another for processing an augmented view of the original image. The input images are divided into patches and fed through the encoder. The proposed framework is evaluated on public CT and X-ray datasets. The proposed system confirms its superiority over state-of-the-art methods on CT and X-ray data in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, specificity, and F1 score. Furthermore, the proposed system also exhibits good robustness when a small portion of training data is allocated.
Keywords: COVID-19; X-ray images; computed tomography; deep learning; vision transformer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
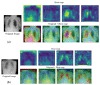
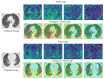
Similar articles
-
IEViT: An enhanced vision transformer architecture for chest X-ray image classification.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Nov;226:107141. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.107141. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022. PMID: 36162246
-
A deep learning-based framework (Co-ReTr) for auto-segmentation of non-small cell-lung cancer in computed tomography images.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Mar;25(3):e14297. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14297. Epub 2024 Feb 19. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38373289 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid explainable ensemble transformer encoder for pneumonia identification from chest X-ray images.J Adv Res. 2023 Jun;48:191-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.021. Epub 2022 Sep 7. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36084812 Free PMC article.
-
A review of deep learning-based detection methods for COVID-19.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Apr;143:105233. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105233. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35180499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis: A comprehensive review of pre-trained deep learning models based on feature extraction algorithm.Results Eng. 2023 Jun;18:101020. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101020. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Results Eng. 2023. PMID: 36945336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CCTCOVID: COVID-19 detection from chest X-ray images using Compact Convolutional Transformers.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 27;11:1025746. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1025746. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36923036 Free PMC article.
-
SCovNet: A skip connection-based feature union deep learning technique with statistical approach analysis for the detection of COVID-19.Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2023 Jan-Mar;43(1):352-368. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2023.01.005. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 36819118 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting EfficientNet, ViT, and gMLP for COVID-19 Detection in Ultrasound Imagery.J Pers Med. 2022 Oct 12;12(10):1707. doi: 10.3390/jpm12101707. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36294846 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Network Selection and Optimized Information Fusion for Enhanced COVID-19 Detection: A Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 21;15(14):1830. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15141830. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of Severe Lung Infection on Chest Radiographs of COVID-19 Patients: Robustness of AI Models across Multi-Institutional Data.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;14(3):341. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030341. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- False-Negative Results of Initial RT-PCR Assays for COVID-19: A Systematic Review. [(accessed on 14 February 2021)]. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0242958. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

