Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Electrocardiogram Estimates Left Atrium Enlargement as a Predictor of Future Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 35207802
- PMCID: PMC8879964
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12020315
Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Electrocardiogram Estimates Left Atrium Enlargement as a Predictor of Future Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
Background: Left atrium enlargement (LAE) can be used as a predictor of future cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension (HTN) and atrial fibrillation (Afib). Typical electrocardiogram (ECG) changes have been reported in patients with LAE. This study developed a deep learning model (DLM)-enabled ECG system to identify patients with LAE.
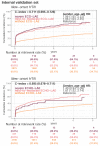
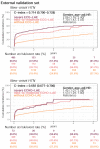
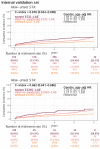
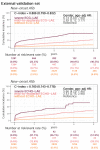
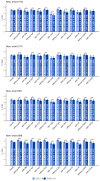
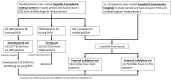
Method: Patients who had ECG records with corresponding echocardiography (ECHO) were included. There were 101,077 ECGs, 20,510 ECGs, 7611 ECGs, and 11,753 ECGs in the development, tuning, internal validation, and external validation sets, respectively. We evaluated the performance of a DLM-enabled ECG for diagnosing LAE and explored the prognostic value of ECG-LAE for new-onset HTN, new-onset stroke (STK), new-onset mitral regurgitation (MR), and new-onset Afib.
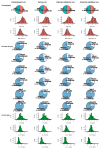
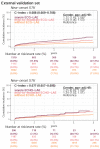
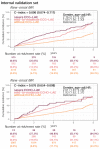
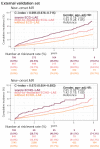
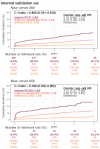
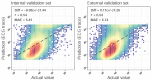
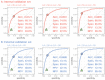
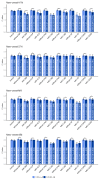
Results: The DLM-enabled ECG achieved AUCs of 0.8127/0.8176 for diagnosing mild LAE, 0.8587/0.8688 for diagnosing moderate LAE, and 0.8899/0.8990 for diagnosing severe LAE in the internal/external validation sets. Notably, ECG-LAE had higher prognostic value compared to ECHO-LAE, which had C-indices of 0.711/0.714 compared to 0.695/0.692 for new-onset HTN, 0.676/0.688 compared to 0.663/0.677 for new-onset STK, 0.696/0.695 compared to 0.676/0.673 for new-onset MR, and 0.800/0.806 compared to 0.786/0.760 for new-onset Afib in internal/external validation sets, respectively.
Conclusions: A DLM-enabled ECG could be considered as a LAE screening tool and provide better prognostic information for related cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; electrocardiogram; left atrium; left atrium enlargement; new-onset atrial fibrillation; new-onset hypertension; new-onset mitral regurgitation; new-onset stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

