Dynamics and Diversity of Microbial Contamination in Poultry Bedding Materials Containing Parts of Medicinal Plants
- PMID: 35207831
- PMCID: PMC8877630
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15041290
Dynamics and Diversity of Microbial Contamination in Poultry Bedding Materials Containing Parts of Medicinal Plants
Abstract
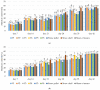
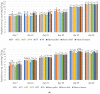
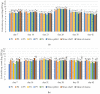
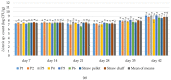
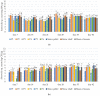
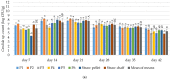
Microorganisms thriving in poultry bedding materials during their exploitation are involved in the development of several diseases and disfunctions of animals. They can also contaminate food products and pose risks to the environment and human health. This study provides an analysis of dynamics and diversity in microbiological contamination observed during the exploitation of poultry bedding materials containing parts of medicinal plants: Satureja hortensis, Origanum vulgare, Melissa officinalis, Salvia officinalis, and Thymus vulgaris, compared with standard types of beddings: straw chaff and straw pellets. The research was carried out in two 42-day experimental cycles involving in total 2400 broiler chickens. Each week, the total count of mesophilic bacteria, fungi and yeasts, the presumptive presence and count of Staphylococcus sp., Escherichia sp., Listeria sp., Salmonella sp., and Candida sp. were determined by culturing on selective media, along with pH and moisture measurements. After 35 days of the experiment, a reduction of the total count of mesophilic bacteria above 1 log compared to the control (11.86 vs. 13.02 log CFU/g) was observed. As the count of yeasts decreased after 21 days, an increase in the total count of bacteria was reported, which indicates a strong competition between microorganisms. The results improve our understanding of the temporal effects of using materials containing parts of medicinal plants on the microbial contamination in poultry litter.
Keywords: Candida; Escherichia; Listeria; Origanum vulgare; Salmonella; Satureja hortensis; Staphylococcus; broiler house; pellets; poultry litter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microbial Contamination of Bedding Material: One Health in Poultry Production.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 8;19(24):16508. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416508. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36554388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of broiler litter with reference to the microbial composition as assessed by using 16S rRNA and functional gene markers.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Feb;69(2):901-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.2.901-908.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12571010 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of rosmarinic acid content in some plants of Labiatae family.Pharmacogn Mag. 2012 Jan;8(29):37-41. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.93316. Pharmacogn Mag. 2012. PMID: 22438661 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of applying Safe2O poultry wash to broiler wings on shelf life, Listeria monocytogenes, Pseudomonads, Staphylococcus species, and psychrotrophic bacteria levels after three, seven, and ten days of storage.Poult Sci. 2004 Jun;83(6):1047-50. doi: 10.1093/ps/83.6.1047. Poult Sci. 2004. PMID: 15206635
-
How Safe is Chicken Litter for Land Application as an Organic Fertilizer? A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep 20;16(19):3521. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16193521. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31547196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Succession, Replacement, and Modification of Chicken Litter Microbiota.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Dec 20;88(24):e0180922. doi: 10.1128/aem.01809-22. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36468876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Gateway to Poultry Production and Products. [(accessed on 6 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/poultry-production-products/production/en/
-
- OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030. [(accessed on 6 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/CB5332EN/Meat.pdf.
-
- European Commission European Citizens Initiative on “End the Cage Age”. [(accessed on 6 December 2021)]. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/QANDA_21_3298.
-
- Chen Z., Jiang X. Microbiological Safety of Chicken Litter or Chicken Litter-Based Organic Fertilizers: A Review. Agriculture. 2014;4:1–29. doi: 10.3390/agriculture4010001. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

