Volatile Analysis of Wuliangye Baijiu by LiChrolut EN SPE Fractionation Coupled with Comprehensive GC×GC-TOFMS
- PMID: 35209103
- PMCID: PMC8878284
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27041318
Volatile Analysis of Wuliangye Baijiu by LiChrolut EN SPE Fractionation Coupled with Comprehensive GC×GC-TOFMS
Abstract
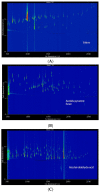
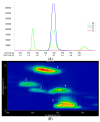
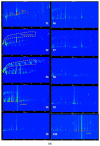
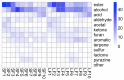
Wuliangye baijiu is one of the most famous Chinese liquors with a protected geographical indication. This study used LiChrolut® EN-based solid-phase extraction (SPE) and fractionation combined with comprehensive two-dimensional chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC×GC-TOFMS) to unveil its volatile composition. The volatiles were isolated with LiChrolut® EN-based SPE and traditional liquid-liquid extraction (LLE). The neutral/basic fractions from LLE and the SPE were fractionated on a LiChrolut® EN SPE column and analyzed by comprehensive GC×GC-TOFMS. Compared with LLE, more esters and alcohols were detected in the SPE-based extraction. The SPE fractionation and GC×GC-TOFMS analysis resulted in the identification of about 500 volatile compounds in more than 3000 peaks of the Wuliangye baijiu. The approach simplifies the complex baijiu composition into functional group-based fractions for reliable identification and analysis. This study provided a confidence volatile identification approach for Chinese baijiu based on the SPE fractionation GC×GC-TOFMS.
Keywords: GC×GC-TOFMS; LiChrolut® EN SPE; Wuliangye; baijiu; volatile fractionation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tandem Solid-Phase Extraction Columns for Simultaneous Aroma Extraction and Fractionation of Wuliangye and Other Baijiu.Molecules. 2021 Oct 4;26(19):6030. doi: 10.3390/molecules26196030. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641574 Free PMC article.
-
Three Extraction Methods in Combination with GC×GC-TOFMS for the Detailed Investigation of Volatiles in Chinese Herbaceous Aroma-Type Baijiu.Molecules. 2020 Sep 27;25(19):4429. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194429. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32992447 Free PMC article.
-
Headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with GC×GC-TOFMS for the analysis of volatile compounds of Coptis species rhizomes.J Sep Sci. 2011 May;34(10):1157-66. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201100022. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Sep Sci. 2011. PMID: 21491598
-
Application of gas chromatography to analysis of spirit-based alcoholic beverages.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2015;45(3):201-25. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2014.904732. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25849822 Review.
-
Current situation, trend, and prospects of research on functional components from by-products of baijiu production: A review.Food Res Int. 2024 Mar;180:114032. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114032. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38395586 Review.
Cited by
-
Wuliangye Baijiu but not ethanol reduces cardiovascular disease risks in a zebrafish thrombosis model.NPJ Sci Food. 2022 Dec 5;6(1):55. doi: 10.1038/s41538-022-00170-2. NPJ Sci Food. 2022. PMID: 36470888 Free PMC article.
-
A two-step framework integrating lasso and Relaxed Lasso for resolving multidimensional collinearity in Chinese baijiu aging research.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 27;10(17):e36871. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36871. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281622 Free PMC article.
-
Discrimination and characterization analysis of key flavor compounds from Tianshui Zanthoxylum bungeanum shells and seeds by GC×GC-TOFMS and chemometrics.Food Chem X. 2025 Jul 8;29:102765. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102765. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40686880 Free PMC article.
-
High-Coverage Profiling of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Using Bromine Isotope Labeling and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry.Metabolites. 2025 Jul 9;15(7):464. doi: 10.3390/metabo15070464. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40710564 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus multifaciens sp. nov., a Crucial and Highly-Active Flavor and Protease Producer Isolated from the qu-Starter of Chinese Wuliangye Baijiu.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 25;13(5):993. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13050993. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He Y.X., Liu Z.P., Qian M., Yu X.W., Xu Y., Chen S. Unraveling the chemosensory characteristics of strong-aroma type Baijiu from different regions using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry and descriptive sensory analysis. Food Chem. 2020;331:127335. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127335. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zheng X.W., Han B.Z. Baijiu (白酒), Chinese liquor: History, classfication and manufacture. J. Ethn. Foods. 2016;3:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jef.2016.03.001. - DOI
-
- Engel W., Bahr W., Schieberle P. Solvent assisted flavour evaporation—A new and versatile technique for the careful and direct isolation of aroma compounds from complex food matrices. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 1999;209:237–241. doi: 10.1007/s002170050486. - DOI
-
- Andrade-Eiroa A., Canle M., Leroy-Cancellieri V., Cerda V. Solid-phase extraction of organic compounds: A critical review (Part I) TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016;80:641–654. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2015.08.015. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

