PLLA Coating of Active Implants for Dual Drug Release
- PMID: 35209205
- PMCID: PMC8875406
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27041417
PLLA Coating of Active Implants for Dual Drug Release
Abstract
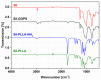
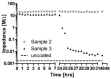
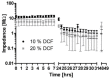
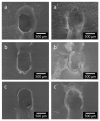
Cochlear implants, like other active implants, rely on precise and effective electrical stimulation of the target tissue but become encapsulated by different amounts of fibrous tissue. The current study aimed at the development of a dual drug release from a PLLA coating and from the bulk material to address short-term and long-lasting release of anti-inflammatory drugs. Inner-ear cytocompatibility of drugs was studied in vitro. A PLLA coating (containing diclofenac) of medical-grade silicone (containing 5% dexamethasone) was developed and release profiles were determined. The influence of different coating thicknesses (2.5, 5 and 10 µm) and loadings (10% and 20% diclofenac) on impedances of electrical contacts were measured with and without pulsatile electrical stimulation. Diclofenac can be applied to the inner ear at concentrations of or below 4 × 10-5 mol/L. Release of dexamethasone from the silicone is diminished by surface coating but not blocked. Addition of 20% diclofenac enhances the dexamethasone release again. All PLLA coatings serve as insulator. This can be overcome by using removable masking on the contacts during the coating process. Dual drug release with different kinetics can be realized by adding drug-loaded coatings to drug-loaded silicone arrays without compromising electrical stimulation.
Keywords: PLLA coating; cochlear implant; diclofenac; dual drug delivery; impedance measurements; spiral ganglion neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



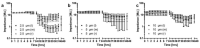
References
-
- Scheper V., Paasche G., Miller J.M., Warnecke A., Berkingali N., Lenarz T., Stöver T. Effects of delayed treatment with combined GDNF and continuous electrical stimulation on spiral ganglion cell survival in deafened guinea pigs. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009;87:1389–1399. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21964. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

