Serum Thioredoxin-80 is associated with age, ApoE4, and neuropathological biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: a potential early sign of AD
- PMID: 35209952
- PMCID: PMC8876266
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-022-00979-9
Serum Thioredoxin-80 is associated with age, ApoE4, and neuropathological biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: a potential early sign of AD
Abstract
Background: Thioredoxin-80 (Trx80) is a cleavage product from the redox-active protein Thioredoxin-1 and has been previously described as a pro-inflammatory cytokine secreted by immune cells. Previous studies in our group reported that Trx80 levels are depleted in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains. However, no studies so far have investigated peripheral Trx80 levels in the context of AD pathology and whether could be associated with the main known AD risk factors and biomarkers.
Methods: Trx80 was measured in serum samples from participants from two different cohorts: the observational memory clinic biobank (GEDOC) (N = 99) with AD CSF biomarker data was available and the population-based lifestyle multidomain intervention trial Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability (FINGER) (N = 47), with neuroimaging data and blood markers of inflammation available. The GEDOC cohort consists of participants diagnosed with subjective cognitive impairment (SCI), mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and AD, whereas the FINGER participants are older adults at-risk of dementia, but without substantial cognitive impairment. One-way ANOVA and multiple comparison tests were used to assess the levels of Trx80 between groups. Linear regression models were used to explore associations of Trx80 with cognition, AD CSF biomarkers (Aβ42, t-tau, p-tau and p-tau/t-tau ratio), inflammatory cytokines, and neuroimaging markers.
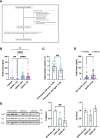
Results: In the GEDOC cohort, Trx80 was associated to p-tau/t-tau ratio in the MCI group. In the FINGER cohort, serum Trx80 levels correlated with lower hippocampal volume and higher pro-inflammatory cytokine levels. In both GEDOC and FINGER cohorts, ApoE4 carriers had significantly higher serum Trx80 levels compared to non-ApoE4 carriers. However, Trx80 levels in the brain were further decreased in AD patients with ApoE4 genotype.
Conclusion: We report that serum Trx80 levels are associated to AD disease stage as well as to several risk factors for AD such as age and ApoE4 genotype, which suggests that Trx80 could have potential as serum AD biomarker. Increased serum Trx80 and decreased brain Trx80 levels was particularly seen in ApoE4 carriers. Whether this could contribute to the mechanism by which ApoE4 show increased vulnerability to develop AD would need to be further investigated.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01041989 . Registered on 4 January 2010-retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Aging; Alzheimer’s disease; ApoE4; Dementia; Inflammation; Thioredoxin-80.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MMB, de Strooper B, Frisoni GB, Salloway S, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2016;388(10043):505–517. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K, Zetterberg H. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: current status and prospects for the future. J Intern Med. 2018;284(6):643–663. - PubMed
-
- Loera-Valencia R, Piras A, Ismail MAM, Manchanda S, Eyjolfsdottir H, Saido TC, et al. Targeting Alzheimer’s disease with gene and cell therapies. J Intern Med. 2018;284(1):2–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

