Partial Ablation of Postsynaptic Dopamine D2 Receptors in the Central Nucleus of the Amygdala Increases Risk Avoidance in Exploratory Tasks
- PMID: 35210287
- PMCID: PMC8925651
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0528-21.2022
Partial Ablation of Postsynaptic Dopamine D2 Receptors in the Central Nucleus of the Amygdala Increases Risk Avoidance in Exploratory Tasks
Abstract
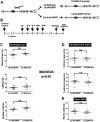
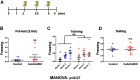
The central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) is involved in the expression of fear and has been implicated in several anxiety disorders. This structure is densely innervated by DAergic projections that impinge on amygdalar neurons expressing various dopamine (DA) receptor subtypes, including D2 receptors (D2Rs). Although various pharmacological approaches have assessed the role of D2Rs in the CeA, the actual participation of postsynaptic D2Rs in the CeA to defensive behaviors remains unclear. Here, we investigated the distribution of D2Rs in the CeA and their role in modifying neuronal activity and fear related behaviors in mice. First, using the mouse reporter strain D2R-EGFP, we verified that D2Rs are present both in neurons of the CeA and in A10 dorsocaudal (A10dc) DAergic neurons that innervate the CeA. Moreover, we showed that pharmacological stimulation of D2Rs increases the activity of protein kinase C (PKC)δ cells present in the CeA, a type of neuron previously associated with reduced defensive behaviors. Finally, using a molecular genetics approach that discriminates postsynaptic D2Rs from presynaptic D2 autoreceptors, we demonstrated that mice carrying targeted deletions of postsynaptic D2Rs in the CeA display increased risk avoidance in exploratory tasks. Together, our results indicate that postsynaptic D2Rs in the CeA attenuate behavioral reactions to potential environmental threats.
Copyright © 2022 Casey et al.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dopamine D1 or D2 receptor-expressing neurons in the central nervous system.Addict Biol. 2018 Mar;23(2):569-584. doi: 10.1111/adb.12512. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Addict Biol. 2018. PMID: 28436559 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol intake enhances glutamatergic transmission from D2 receptor-expressing afferents onto D1 receptor-expressing medium spiny neurons in the dorsomedial striatum.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 May;44(6):1123-1131. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0332-9. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30733568 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D2 Receptors in the Paraventricular Thalamus Attenuate Cocaine Locomotor Sensitization.eNeuro. 2017 Oct 24;4(5):ENEURO.0227-17.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0227-17.2017. eCollection 2017 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 29071300 Free PMC article.
-
Getting specialized: presynaptic and postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptors.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;9(1):53-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.12.002. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19138563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restructuring of basal ganglia circuitry and associated behaviors triggered by low striatal D2 receptor expression: implications for substance use disorders.Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Jan;16(1):56-70. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12361. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 27860248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo multiplex imaging of dynamic neurochemical networks with designed far-red dopamine sensors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 23:2024.12.22.629999. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.22.629999. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39763912 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Inhibitory effects of dopamine agonists on pain-responsive neurons in the central nucleus of the amygdala.J Neurophysiol. 2025 Jun 1;133(6):1947-1954. doi: 10.1152/jn.00135.2025. Epub 2025 May 27. J Neurophysiol. 2025. PMID: 40423681 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
