Incidence and management of CAR-T neurotoxicity in patients with multiple myeloma treated with ciltacabtagene autoleucel in CARTITUDE studies
- PMID: 35210399
- PMCID: PMC8873238
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-022-00629-1
Incidence and management of CAR-T neurotoxicity in patients with multiple myeloma treated with ciltacabtagene autoleucel in CARTITUDE studies
Abstract
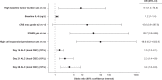
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are highly effective for multiple myeloma (MM) but their impressive efficacy is associated with treatment-related neurotoxicities in some patients. In CARTITUDE-1, 5% of patients with MM reported movement and neurocognitive treatment-emergent adverse events (MNTs) with ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel), a B-cell maturation antigen-targeted CAR T-cell therapy. We assessed the associated factors for MNTs in CARTITUDE-1. Based on common features, patients who experienced MNTs were characterized by the presence of a combination of at least two variables: high tumor burden, grade ≥2 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) or any grade immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) after cilta-cel infusion, and high CAR T-cell expansion/persistence. Strategies were implemented across the cilta-cel development program to monitor and manage patients with MNTs, including enhanced bridging therapy to reduce baseline tumor burden, early aggressive treatment of CRS and ICANS, handwriting assessments for early symptom detection, and extended monitoring/reporting time for neurotoxicity beyond 100 days post-infusion. After successful implementation of these strategies, the incidence of MNTs was reduced from 5% to <1% across the cilta-cel program, supporting its favorable benefit-risk profile for treatment of MM.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AC served in a consulting or advisory role for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech/Roche, Janssen, and Takeda, and received patents, royalties, and other intellectual property from Novartis. SJ is a consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Merck, Sanofi, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals. SP is supported by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) (R01 CA244899, CA252222) and receives research funding from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Karyopharm. BS is an inventor on United States Provisional Patent Application No.: US20210181179A1 “Diagnosis and treatment of immunotherapy-induced neurotoxicity” filed by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, served in a consulting or advisory role for Celgene, Janssen, Legend Biotech, Incyte, and In8bio, and received research funding from ADC Therapeutics. JGP-L served in a consulting or advisory role for Janssen, served in speakers bureau for Eisai, and received research funding from DNAtrix. NWCJvdD received grant support and advisory board fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Amgen, advisory board fees from Takeda, Servier, Bayer, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and Sanofi, and grant support from Cellectis. BA served in a consulting or advisory role for Amgen, Celgene, and Janssen-Cilag, received travel expenses from Amgen, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Sanofi, and Takeda, received honoraria from Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Sanofi, and Takeda, and received research funding from Janssen-Cilag. M-VM received consulting fees from Janssen-Cilag, GlaxoSmithKline, Celgene, Amgen, Regeneron, Pfizer, AbbVie, Takeda, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi, Oncopeptides, and Adaptive Biotechnologies. DM, KCDB, JMS, HV, LM, EL, IC, NL, YO, EZ, and CL are employees of Janssen. CCJ is an employee of Janssen and a consultant physician at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (New York, NY, USA). LP, MA, and DG are employees of Legend Biotech. AJ served in a consulting or advisory role for and received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Karyopharm Therapeutics, and Sanofi. HE served in a consulting or advisory role for Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Takeda, received travel expenses from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda, received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Takeda, and received research funding from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, and Janssen.
Figures




References
-
- FDA Adverse event reporting system public dashboard. 2020. https://fis.fda.gov.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

