A fast Myosin super enhancer dictates muscle fiber phenotype through competitive interactions with Myosin genes
- PMID: 35210422
- PMCID: PMC8873246
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28666-1
A fast Myosin super enhancer dictates muscle fiber phenotype through competitive interactions with Myosin genes
Abstract
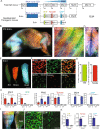
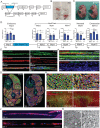
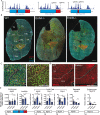
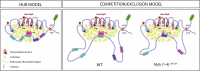
The contractile properties of adult myofibers are shaped by their Myosin heavy chain isoform content. Here, we identify by snATAC-seq a 42 kb super-enhancer at the locus regrouping the fast Myosin genes. By 4C-seq we show that active fast Myosin promoters interact with this super-enhancer by DNA looping, leading to the activation of a single promoter per nucleus. A rainbow mouse transgenic model of the locus including the super-enhancer recapitulates the endogenous spatio-temporal expression of adult fast Myosin genes. In situ deletion of the super-enhancer by CRISPR/Cas9 editing demonstrates its major role in the control of associated fast Myosin genes, and deletion of two fast Myosin genes at the locus reveals an active competition of the promoters for the shared super-enhancer. Last, by disrupting the organization of fast Myosin, we uncover positional heterogeneity within limb skeletal muscles that may underlie selective muscle susceptibility to damage in certain myopathies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Emery AE. Muscular dystrophy into the new millennium. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2002;12:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Mantilla CB, Sieck GC. Invited review: mechanisms underlying motor unit plasticity in the respiratory system. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003;94:1230–1241. - PubMed
-
- Kanning KC, Kaplan A, Henderson CE. Motor neuron diversity in development and disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2010;33:409–440. - PubMed
-
- Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol. Rev. 2011;91:1447–1531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

