Local inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling improves Th17/Treg balance but not joint pathology during experimental arthritis
- PMID: 35210510
- PMCID: PMC8873460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-07075-w
Local inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling improves Th17/Treg balance but not joint pathology during experimental arthritis
Abstract
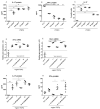
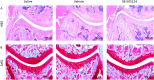
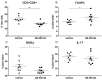
TGF-β1 is an important growth factor to promote the differentiation of T helper 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg). The potential of TGF-β1 as therapeutic target in T cell-mediated diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is unclear. We investigated the effect of TGF-β1 inhibition on murine Th17 differentiation in vitro, on human RA synovial explants ex vivo, and on the development of experimental arthritis in vivo. Murine splenocytes were differentiated into Th17 cells, and the effect of the TGF-βRI inhibitor SB-505124 was studied. Synovial biopsies were cultured in the presence or absence of SB-505124. Experimental arthritis was induced in C57Bl6 mice and treated daily with SB-505124. Flow cytometry analysis was performed to measure different T cell subsets. Histological sections were analysed to determine joint inflammation and destruction. SB-505124 potently reduced murine Th17 differentiation by decreasing Il17a and Rorc gene expression and IL-17 protein production. SB-505124 significantly suppressed IL-6 production by synovial explants. In vivo, SB-505124 reduced Th17 numbers, while increased numbers of Tregs were observed. Despite this skewed Th17/Treg balance, SB-505124 treatment did not result in suppression of joint inflammation and destruction. Blocking TGF-β1 signalling suppresses Th17 differentiation and improves the Th17/Treg balance. However, local SB-505124 treatment does not suppress experimental arthritis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
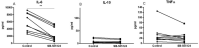
Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity of Treg/Th17 According to Cancer Progression and Modification in Biliary Tract Cancers via Self-Producing Cytokines.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Oct;65(10):2937-2948. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-06011-9. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. PMID: 31853779
-
Effects of thalidomide on Th17, Treg cells and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway in a mouse model of systemic sclerosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Mar;23(3):406-419. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13769. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 31840939
-
TGF-beta-exposed plasmacytoid dendritic cells participate in Th17 commitment.J Immunol. 2011 Jun 1;186(11):6157-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002497. Epub 2011 Apr 25. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21518970 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 in regulatory T cell biology.Sci Immunol. 2022 Mar 18;7(69):eabi4613. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abi4613. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Sci Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35302863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role, targets and mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine in regulating the balance of T helper type 17/regulatory Tcells in rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2023 Apr;26(4):613-624. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14560. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 36680325 Review.
Cited by
-
Augmenting regulatory T cells: new therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 23;15:1312919. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1312919. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38322264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxygen regulates ILC3 antigen presentation potential and pregnancy-related hormone actions.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022 Jul 29;20(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12958-022-00979-2. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35906658 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of serum miR-135a in patients with allergic rhinitis and its relationship with Treg/Th17 balance.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025 Jan;41(1):e12918. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12918. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39661490 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin: A Bone-Derived Protein Involved in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis Immunopathology.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 9;13(3):502. doi: 10.3390/biom13030502. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β inhibition restores hematopoiesis and immune balance via bone marrow EPCs in aplastic anemia.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Jun;57(6):1324-1338. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01483-4. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40588527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cope AP, Schulze-Koops H, Aringer M. The central role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007;25:S4–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

