Correlation between antibiotic consumption and the occurrence of multidrug-resistant organisms in a Malaysian tertiary hospital: a 3-year observational study
- PMID: 35210515
- PMCID: PMC8873402
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-07142-2
Correlation between antibiotic consumption and the occurrence of multidrug-resistant organisms in a Malaysian tertiary hospital: a 3-year observational study
Abstract
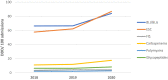
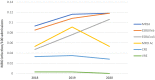
Inappropriate use of antibiotics has been shown to contribute to the occurrence of multidrug-resistant organisms (MROs). A surveillance study was performed in the largest tertiary care hospital in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, from 2018 to 2020 to observe the trends of broad-spectrum antibiotics (beta-lactam/beta-lactamases inhibitors (BL/BLI), extended-spectrum cephalosporins (ESC), and fluoroquinolones (FQ)) and antibiotics against MRO (carbapenems, polymyxins, and glycopeptides) usage and the correlation between antibiotic consumption and MROs. The correlation between 3-year trends of antibiotic consumption (defined daily dose (DDD)/100 admissions) with MRO infection cases (per 100 admissions) was determined using a Jonckheere-Terpstra test and a Pearson's Correlation coefficient. The antimicrobial resistance trend demonstrated a positive correlation between ESC and FQ towards the development of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella spp, ESBL-producing Escherichia coli (E. coli), and MRO Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii). Increasing carbapenem consumption was positively correlated with the occurrence of ESBL-producing Klebsiella spp and E. coli. Polymyxin use was positively correlated with ESBL-producing Klebsiella spp, MRO A. baumannii, and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. The findings reinforced concerns regarding the association between MRO development, especially with a surge in ESC and FQ consumption. Stricter use of antimicrobials is thus crucial to minimise the risk of emerging resistant organisms.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS) Report: Early Implementation 2017–2018. (World Health Organization, 2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

