ITK independent development of Th17 responses during hypersensitivity pneumonitis driven lung inflammation
- PMID: 35210549
- PMCID: PMC8873479
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03109-1
ITK independent development of Th17 responses during hypersensitivity pneumonitis driven lung inflammation
Abstract
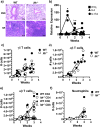
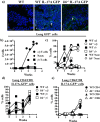
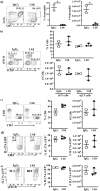
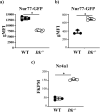
T helper 17 (Th17) cells develop in response to T cell receptor signals (TCR) in the presence of specific environments, and produce the inflammatory cytokine IL17A. These cells have been implicated in a number of inflammatory diseases and represent a potential target for ameliorating such diseases. The kinase ITK, a critical regulator of TCR signals, has been shown to be required for the development of Th17 cells. However, we show here that lung inflammation induced by Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula (SR) induced Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (SR-HP) results in a neutrophil independent, and ITK independent Th17 responses, although ITK signals are required for γδ T cell production of IL17A. Transcriptomic analysis of resultant ITK independent Th17 cells suggest that the SR-HP-induced extrinsic inflammatory signals may override intrinsic T cell signals downstream of ITK to rescue Th17 responses in the absence of ITK. These findings suggest that the ability to pharmaceutically target ITK to suppress Th17 responses may be dependent on the type of inflammation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.A. receives research support from 3M Company. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 11;15:1403155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1403155. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39464896 Free PMC article.
-
Itk-mediated integration of T cell receptor and cytokine signaling regulates the balance between Th17 and regulatory T cells.J Exp Med. 2014 Mar 10;211(3):529-43. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131459. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 24534190 Free PMC article.
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis onset and severity is regulated by CD103 dendritic cell expression.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 19;12(6):e0179678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179678. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28628641 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning T helper cell differentiation by ITK.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):179-185. doi: 10.1042/BST20190486. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32049330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the IL-2 inducible tyrosine kinase ITK and its inhibitors in disease pathogenesis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Oct;98(10):1385-1395. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01958-z. Epub 2020 Aug 18. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32808093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The kinase ITK controls a Ca2+-mediated switch that balances TH17 and Treg cell differentiation.Sci Signal. 2024 Jul 23;17(846):eadh2381. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adh2381. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Sci Signal. 2024. PMID: 39042726 Free PMC article.
-
IL-2-inducible T cell kinase deficiency sustains chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy against tumor cells.J Clin Invest. 2024 Nov 26;135(4):e178558. doi: 10.1172/JCI178558. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39589809 Free PMC article.
-
Exploratory analysis of the key role of immune function changes in BPD.Pediatr Discov. 2024 Dec 21;2(4):e2515. doi: 10.1002/pdi3.2515. eCollection 2024 Dec. Pediatr Discov. 2024. PMID: 40626128 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 11;15:1403155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1403155. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39464896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinman L. A brief history of T(H)17, the first major revision in the T(H)1/T(H)2 hypothesis of T cell-mediated tissue damage. Nat. Med. 2007;13:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Coquet JM, Rausch L, Borst J. The importance of co-stimulation in the orchestration of T helper cell differentiation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015;93:780–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI129422/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AI129422/Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID)
- R01 AI120701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI129422/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 AI132738/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI138570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM096955/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI120701/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- T32 EB023860/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD076210/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- AI138570/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- AI132738/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

