Modeling comparative cost-effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dose fractionation in India
- PMID: 35210596
- PMCID: PMC9117137
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01736-z
Modeling comparative cost-effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dose fractionation in India
Abstract
Given global Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine shortages and inequity of vaccine distributions, fractionation of vaccine doses might be an effective strategy for reducing public health and economic burden, notwithstanding the emergence of new variants of concern. In this study, we developed a multi-scale model incorporating population-level transmission and individual-level vaccination to estimate the costs of hospitalization and vaccination and the economic benefits of reducing COVID-19 deaths due to dose-fractionation strategies in India. We used large-scale survey data of the willingness to pay together with data of vaccine and hospital admission costs to build the model. We found that fractional doses of vaccines could be an economically viable vaccination strategy compared to alternatives of either full-dose vaccination or no vaccination. Dose-sparing strategies could save a large number of lives, even with the emergence of new variants with higher transmissibility.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
B.J.C. consults for AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Moderna, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi Pasteur. B.J.C. is supported by the AIR@innoHK program of the Innovation and Technology Commission of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
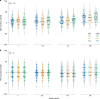
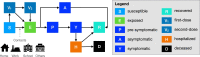
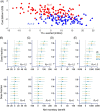
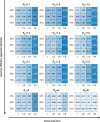
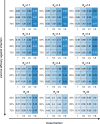
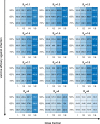

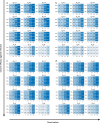
References
-
- COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594...
-
- Zimmer, C., Corum, J., Wee, S.-L. & Kristoffersen, M. Coronavirus Vaccine Tracker. The New York Timeshttps://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/science/coronavirus-vaccine-tra...
-
- Low & middle income. World Bank Group Development Data Group. https://data.worldbank.org/country/XO
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

