The 2017 ACR TI-RADS: pictorial essay
- PMID: 35210664
- PMCID: PMC8864691
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2020.0141
The 2017 ACR TI-RADS: pictorial essay
Abstract
High-resolution ultrasound is the imaging method of choice for the evaluation of thyroid nodules. The method has recently come to be used widely and often, which has increased the rate of thyroid nodule detection. In 2017, the American College of Radiology (ACR) established a risk-stratification system designated the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) to be a practical guide for widespread use, with a single lexicon and standardization of ultrasound reports of thyroid nodules. The objective of this study was to present a practical approach, using examples to illustrate the criteria evaluated by the 2017 ACR TI-RADS, in order to help minimize uncertainties regarding its application by sonographers.
A ultrassonografia de alta resolução é a modalidade de escolha para avaliação de imagem dos nódulos tireoidianos, e sua recente aplicação ampla e difusa tornou a detecção de nódulos tireoidianos mais frequentes. O American College of Radiology (ACR) estabeleceu um sistema de estratificação de risco denominado Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) para ser um guia prático para utilização ampla com um léxico único e padronização de relatórios ultrassonográficos de nódulos tireoidianos. O objetivo deste trabalho é fazer uma abordagem prática com base em exames para ilustrar e exemplificar os critérios avaliados pelo TI-RADS-ACR 2017, a fim de ajudar a reduzir os pontos de dúvidas de sua aplicação pelos profissionais ultrassonografistas.
Keywords: Thyroid diseases; Thyroid gland; Ultrasonography.
Figures

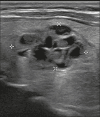

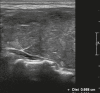

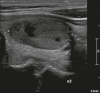
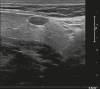
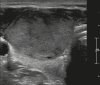
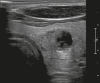
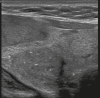
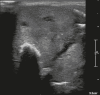
Similar articles
-
A Multidisciplinary Head-to-Head Comparison of American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging and Reporting Data System and American Thyroid Association Ultrasound Risk Stratification Systems.Oncologist. 2020 May;25(5):398-403. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0362. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 31740569 Free PMC article.
-
Does a higher American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (ACR TI-RADS) score forecast an increased risk of malignancy? A correlation study of ACR TI-RADS with FNA cytology in the evaluation of thyroid nodules.Cancer Cytopathol. 2020 Jul;128(7):470-481. doi: 10.1002/cncy.22254. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020. PMID: 32078249
-
Clinical Study of the Prediction of Malignancy in Thyroid Nodules: Modified Score versus 2017 American College of Radiology's Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System Ultrasound Lexicon.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Jul;45(7):1627-1637. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 May 4. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31064698
-
Update on ACR TI-RADS: Successes, Challenges, and Future Directions, From the AJR Special Series on Radiology Reporting and Data Systems.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 Mar;216(3):570-578. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24608. Epub 2021 Jan 21. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021. PMID: 33112199 Review.
-
Diagnostic Performance of American College of Radiology TI-RADS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 Jan;216(1):38-47. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.22691. Epub 2020 Nov 19. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021. PMID: 32603229
Cited by
-
Visualizing thyroid health: a pictorial journey through 2017 ACR TI-RADS and common thyroid pathologies.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jul 23;86(9):5377-5388. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002398. eCollection 2024 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39239024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hashimoto Thyroiditis beyond Cytology: A Correlation between Cytological, Hormonal, Serological, and Radiological Findings.J Thyroid Res. 2023 Jun 19;2023:5707120. doi: 10.1155/2023/5707120. eCollection 2023. J Thyroid Res. 2023. PMID: 37377479 Free PMC article.
-
A model based on C-TIRADS combined with SWE for predicting Bethesda I thyroid nodules.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 30;14:1421088. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1421088. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39281385 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic radiomics in predicting pathologic type for thyroid cancer: a preliminary study using radiomics features for predicting medullary thyroid carcinoma.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 19;16:1428888. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1428888. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40046879 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency ablation compared to surgery for thyroid nodules: A case for office based treatment.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 Jun 18;9(3):e1276. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1276. eCollection 2024 Jun. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38895024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ezzat S, Sarti DA, Cain DR, et al. Thyroid incidentalomas. Prevalence by palpation and ultrasonography. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154:1838–1840. - PubMed
-
- Nam-Goong IS, Kim HY, Gong G, et al. Ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration of thyroid incidentaloma: correlation with pathological findings. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2004;60:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Ito Y, Miyauchi A, Inoue H, et al. An observational trial for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in Japanese patients. World J Surg. 2010;34:28–35. - PubMed
-
- Tessler FN, Middleton WD, Grant EG, et al. ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): White Paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017;14:587–595. - PubMed
-
- Grant EG, Tessler FN, Hoang JK, et al. Thyroid ultrasound reporting lexicon: White Paper of the ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) Committee. J Am Coll Radiol. 2015;12(12):1272–1279. Pt A. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
